Fourier Imager Network : A deep neural network for hologram reconstruction with superior external generalization
Paper and Code
Apr 22, 2022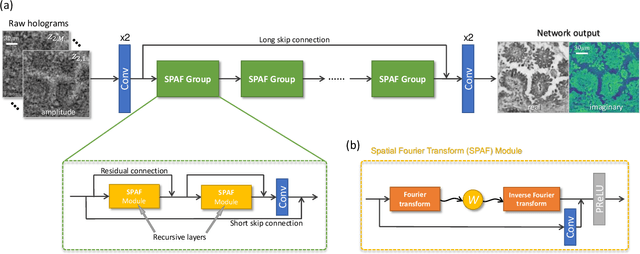
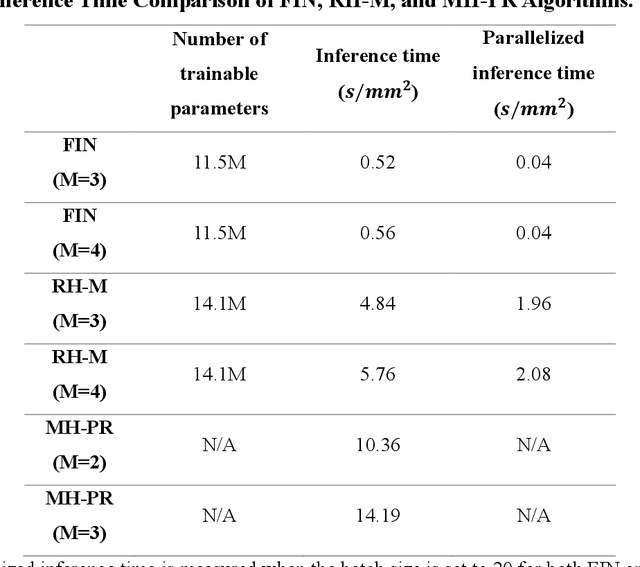
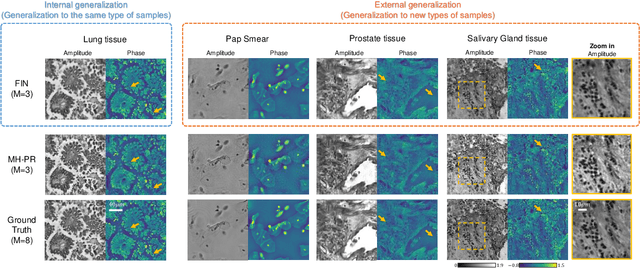
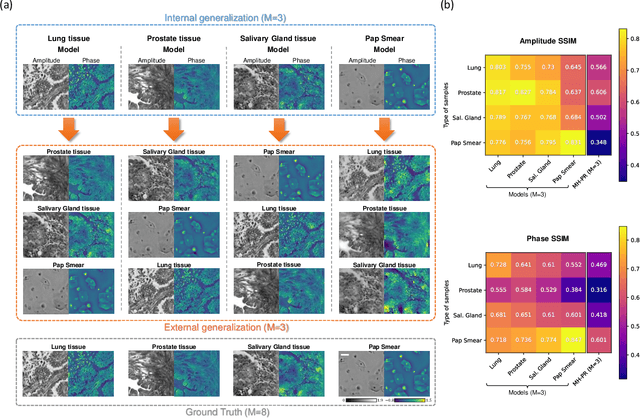
Deep learning-based image reconstruction methods have achieved remarkable success in phase recovery and holographic imaging. However, the generalization of their image reconstruction performance to new types of samples never seen by the network remains a challenge. Here we introduce a deep learning framework, termed Fourier Imager Network (FIN), that can perform end-to-end phase recovery and image reconstruction from raw holograms of new types of samples, exhibiting unprecedented success in external generalization. FIN architecture is based on spatial Fourier transform modules that process the spatial frequencies of its inputs using learnable filters and a global receptive field. Compared with existing convolutional deep neural networks used for hologram reconstruction, FIN exhibits superior generalization to new types of samples, while also being much faster in its image inference speed, completing the hologram reconstruction task in ~0.04 s per 1 mm^2 of the sample area. We experimentally validated the performance of FIN by training it using human lung tissue samples and blindly testing it on human prostate, salivary gland tissue and Pap smear samples, proving its superior external generalization and image reconstruction speed. Beyond holographic microscopy and quantitative phase imaging, FIN and the underlying neural network architecture might open up various new opportunities to design broadly generalizable deep learning models in computational imaging and machine vision fields.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge