FollowNet: Robot Navigation by Following Natural Language Directions with Deep Reinforcement Learning
Paper and Code
May 16, 2018
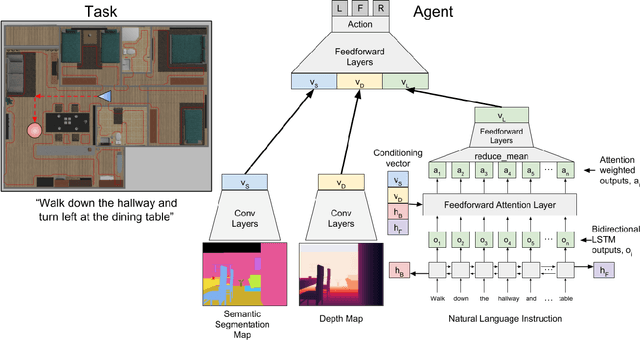
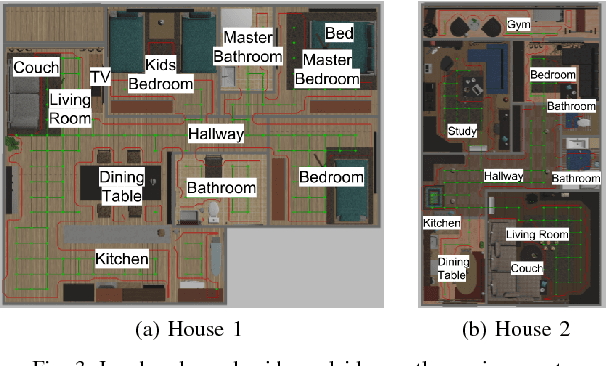
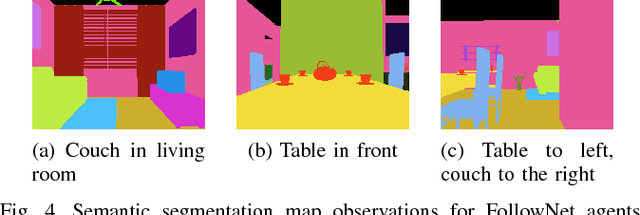
Understanding and following directions provided by humans can enable robots to navigate effectively in unknown situations. We present FollowNet, an end-to-end differentiable neural architecture for learning multi-modal navigation policies. FollowNet maps natural language instructions as well as visual and depth inputs to locomotion primitives. FollowNet processes instructions using an attention mechanism conditioned on its visual and depth input to focus on the relevant parts of the command while performing the navigation task. Deep reinforcement learning (RL) a sparse reward learns simultaneously the state representation, the attention function, and control policies. We evaluate our agent on a dataset of complex natural language directions that guide the agent through a rich and realistic dataset of simulated homes. We show that the FollowNet agent learns to execute previously unseen instructions described with a similar vocabulary, and successfully navigates along paths not encountered during training. The agent shows 30% improvement over a baseline model without the attention mechanism, with 52% success rate at novel instructions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge