Flight Demonstration and Model Validation of a Prototype Variable-Altitude Venus Aerobot
Paper and Code
Nov 11, 2024
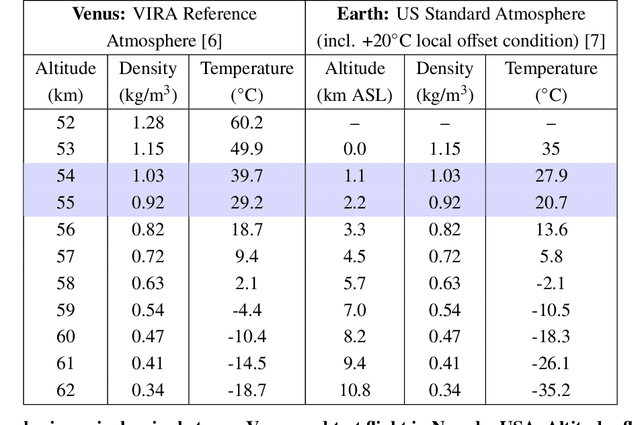
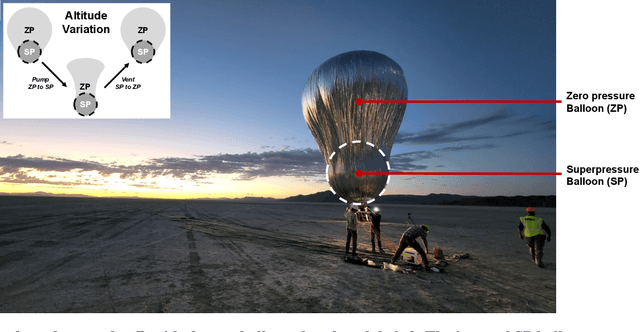
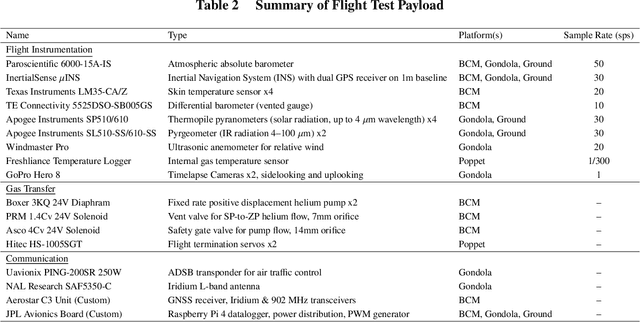
This paper details a significant milestone towards maturing a buoyant aerial robotic platform, or aerobot, for flight in the Venus clouds. We describe two flights of our subscale altitude-controlled aerobot, fabricated from the materials necessary to survive Venus conditions. During these flights over the Nevada Black Rock desert, the prototype flew at the identical atmospheric densities as 54 to 55 km cloud layer altitudes on Venus. We further describe a first-principle aerobot dynamics model which we validate against the Nevada flight data and subsequently employ to predict the performance of future aerobots on Venus. The aerobot discussed in this paper is under JPL development for an in-situ mission flying multiple circumnavigations of Venus, sampling the chemical and physical properties of the planet's atmosphere and also remotely sensing surface properties.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge