Flexible Modeling of Latent Task Structures in Multitask Learning
Paper and Code
Jun 27, 2012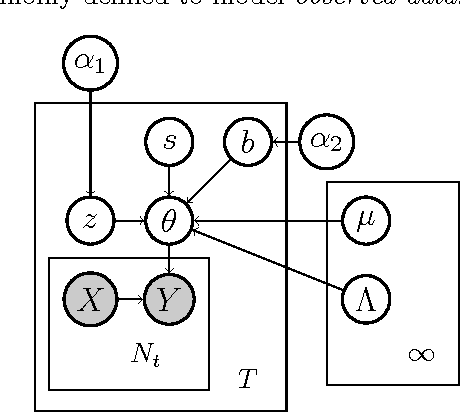
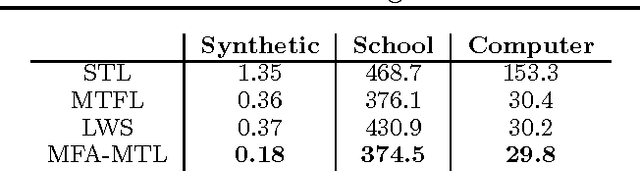
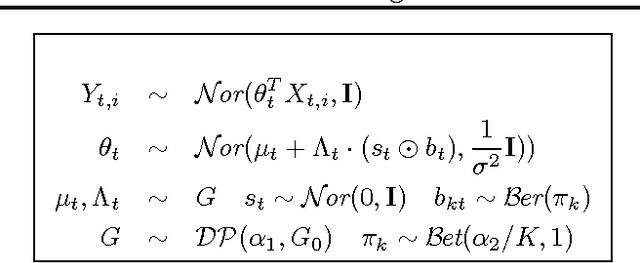
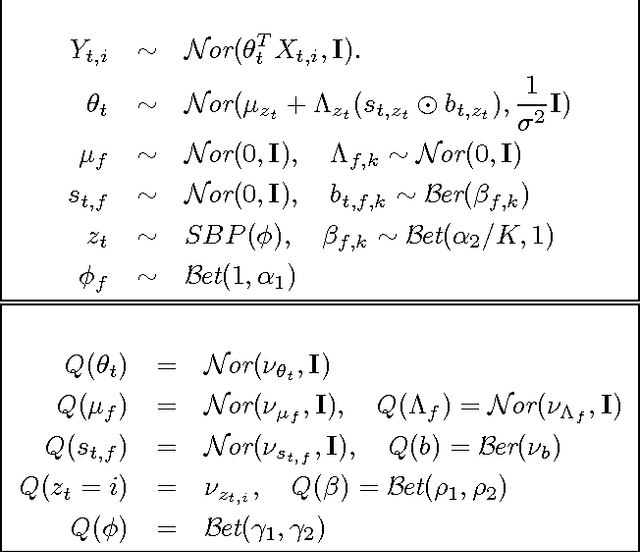
Multitask learning algorithms are typically designed assuming some fixed, a priori known latent structure shared by all the tasks. However, it is usually unclear what type of latent task structure is the most appropriate for a given multitask learning problem. Ideally, the "right" latent task structure should be learned in a data-driven manner. We present a flexible, nonparametric Bayesian model that posits a mixture of factor analyzers structure on the tasks. The nonparametric aspect makes the model expressive enough to subsume many existing models of latent task structures (e.g, mean-regularized tasks, clustered tasks, low-rank or linear/non-linear subspace assumption on tasks, etc.). Moreover, it can also learn more general task structures, addressing the shortcomings of such models. We present a variational inference algorithm for our model. Experimental results on synthetic and real-world datasets, on both regression and classification problems, demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge