Few-Shot Learning with Uncertainty-based Quadruplet Selection for Interference Classification in GNSS Data
Paper and Code
Feb 09, 2024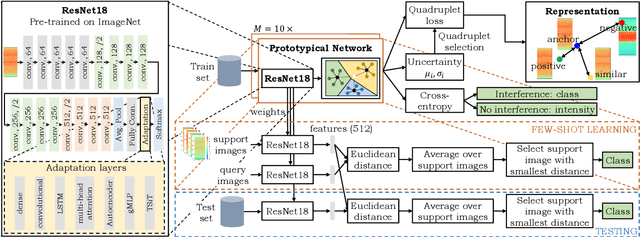
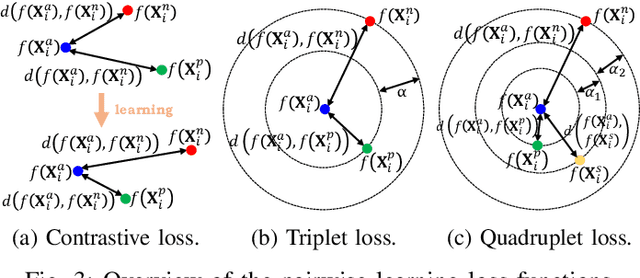
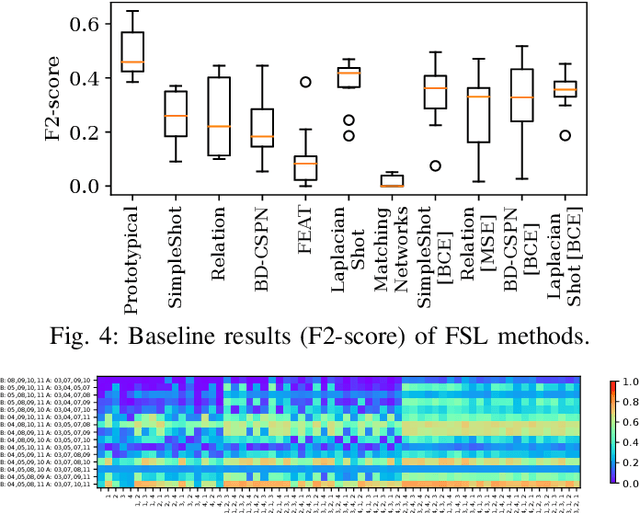
Jamming devices pose a significant threat by disrupting signals from the global navigation satellite system (GNSS), compromising the robustness of accurate positioning. Detecting anomalies in frequency snapshots is crucial to counteract these interferences effectively. The ability to adapt to diverse, unseen interference characteristics is essential for ensuring the reliability of GNSS in real-world applications. In this paper, we propose a few-shot learning (FSL) approach to adapt to new interference classes. Our method employs quadruplet selection for the model to learn representations using various positive and negative interference classes. Furthermore, our quadruplet variant selects pairs based on the aleatoric and epistemic uncertainty to differentiate between similar classes. We recorded a dataset at a motorway with eight interference classes on which our FSL method with quadruplet loss outperforms other FSL techniques in jammer classification accuracy with 97.66%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge