Feedback-Free Resource Scheduling: Towards Flexible Multi-BS Cooperation in FD-RAN
Paper and Code
Feb 25, 2025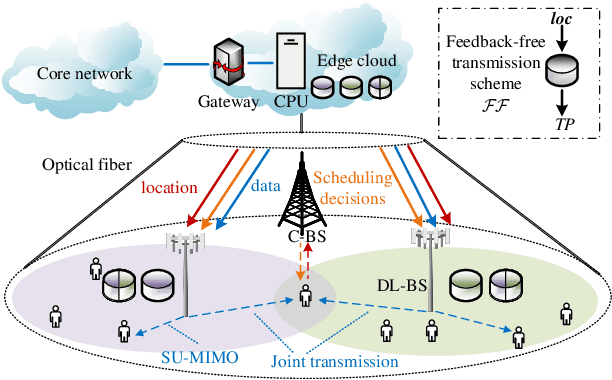
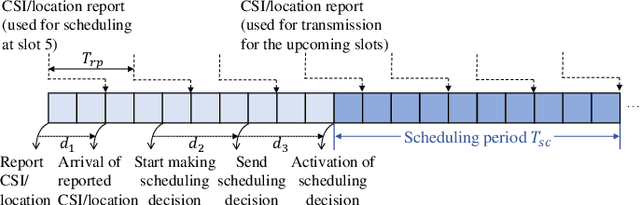
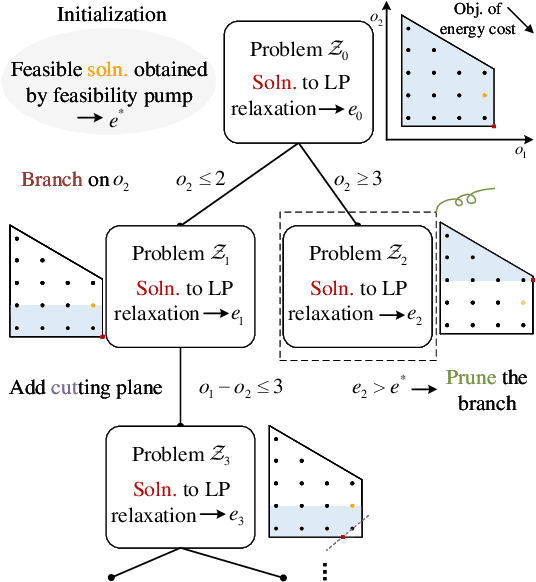
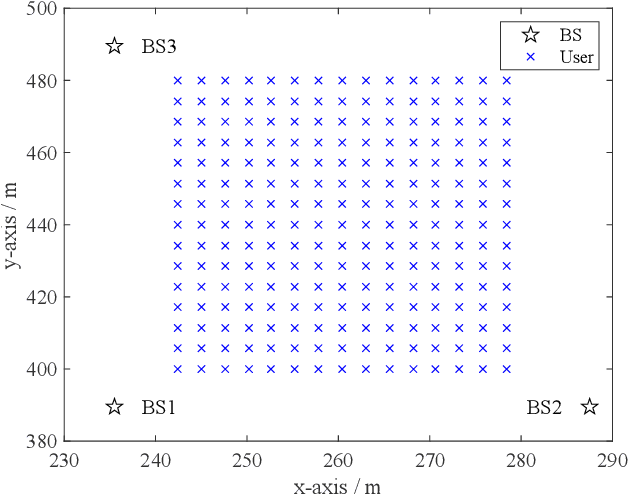
Flexible cooperation among base stations (BSs) is critical to improve resource utilization efficiency and meet personalized user demands. However, its practical implementation is hindered by the current radio access network (RAN), which relies on the coupling of uplink and downlink transmissions and channel state information feedback with inherent issues such as overheads and delays. To overcome these limitations, we consider the fully-decoupled RAN (FD-RAN), in which uplink and downlink networks are independent, and feedback-free MIMO transmission is adopted at the physical layer. To further deliver flexible cooperation in FD-RAN, we investigate the practical scheduling process and study feedback-free downlink multi-BS resource scheduling. The problem is considered based on network load conditions. In heavy-load states where it is impossible for all user demands to be met, an optimal greedy algorithm is proposed, maximizing the weighted sum of user demand satisfaction rates. In light-load states where at least one solution exists to satisfy all user demands, an optimal two-stage resource allocation algorithm is designed to further minimize network energy consumption by leveraging the flexibility of cooperation. Extensive simulations validate the superiority of proposed algorithms in performance and running time, and highlight the potential for realizing flexible cooperation in practice.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge