Federated Mutual Learning
Paper and Code
Jun 27, 2020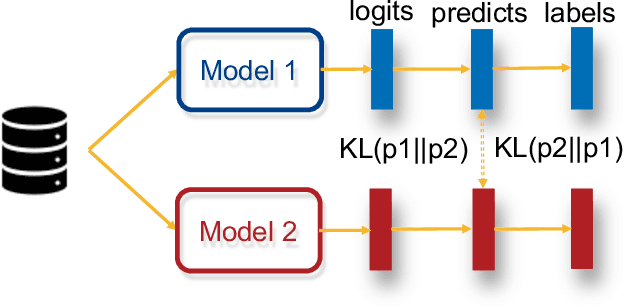
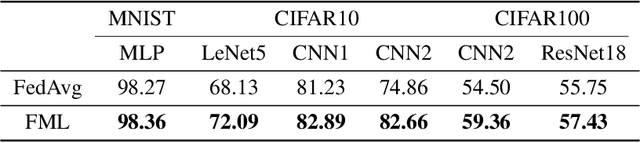
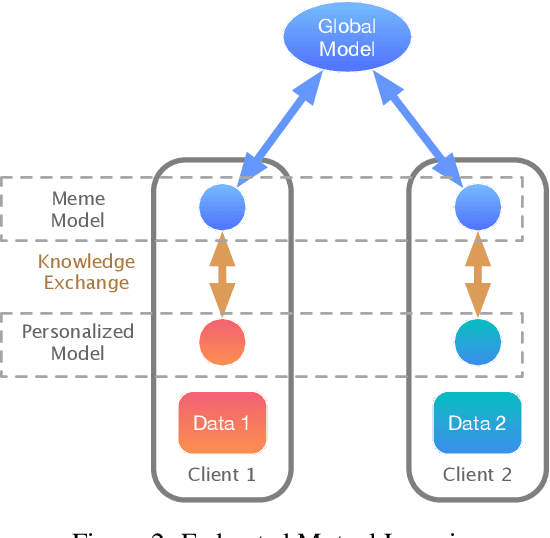
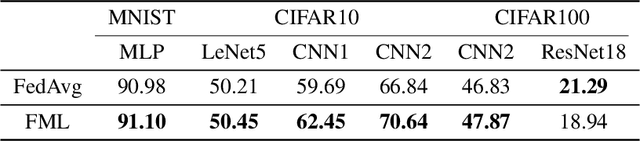
Federated learning enables collaboratively training machine learning models on decentralized data. The three types of heterogeneous natures that is data, model, and objective bring about unique challenges to the canonical federated learning algorithm (FederatedAveraging), where one shared model is produced by and for all clients. First, due to the Non-IIDness of data, the global shared model may perform worse than local models that solely trained on their private data; Second, clients may need to design their own model because of different communication and computing abilities of devices, which is also private property that should be protected; Third, the objective of achieving consensus throughout the training process will compromise the personalities of clients. In this work, we present a novel federated learning paradigm, named Federated Mutual Leaning (FML), dealing with the three heterogeneities. FML allows clients designing their customized models and training independently, thus the Non-IIDness of data is no longer a bug but a feature that clients can be personally served better. Local customized models can benefit from collaboratively training without compromising personalities. Global model does not have to be an out-of-the-box (OOTB) product but a meta-learner which requires local adaptation for new participants. The experiments show that FML can achieve better performance, robustness and communication efficiency than alternatives.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge