Fast Task Inference with Variational Intrinsic Successor Features
Paper and Code
Jun 12, 2019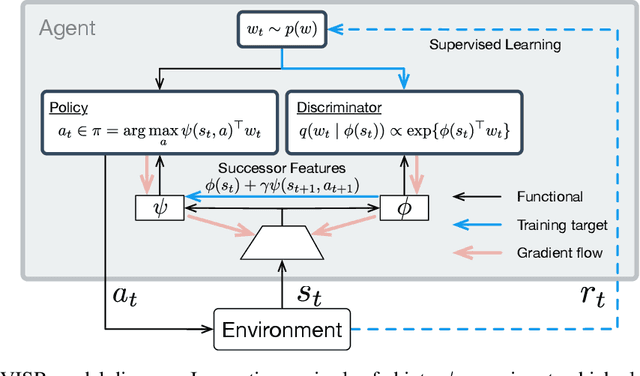
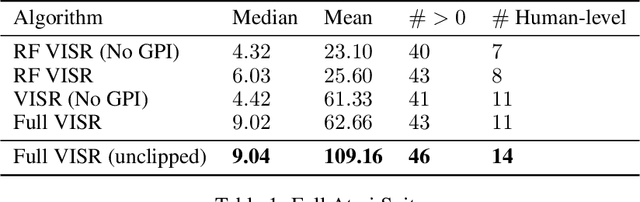
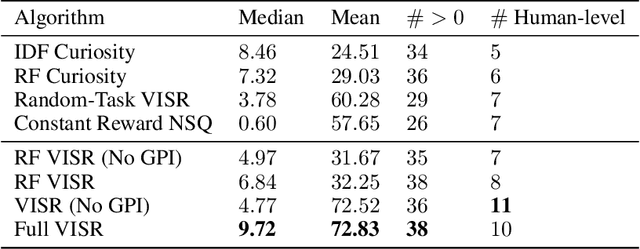
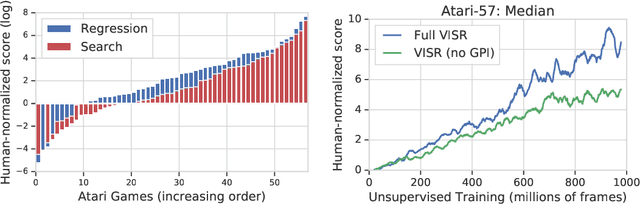
It has been established that diverse behaviors spanning the controllable subspace of an Markov decision process can be trained by rewarding a policy for being distinguishable from other policies \citep{gregor2016variational, eysenbach2018diversity, warde2018unsupervised}. However, one limitation of this formulation is generalizing behaviors beyond the finite set being explicitly learned, as is needed for use on subsequent tasks. Successor features \citep{dayan93improving, barreto2017successor} provide an appealing solution to this generalization problem, but require defining the reward function as linear in some grounded feature space. In this paper, we show that these two techniques can be combined, and that each method solves the other's primary limitation. To do so we introduce Variational Intrinsic Successor FeatuRes (VISR), a novel algorithm which learns controllable features that can be leveraged to provide enhanced generalization and fast task inference through the successor feature framework. We empirically validate VISR on the full Atari suite, in a novel setup wherein the rewards are only exposed briefly after a long unsupervised phase. Achieving human-level performance on 14 games and beating all baselines, we believe VISR represents a step towards agents that rapidly learn from limited feedback.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge