Extend and Explain: Interpreting Very Long Language Models
Paper and Code
Sep 07, 2022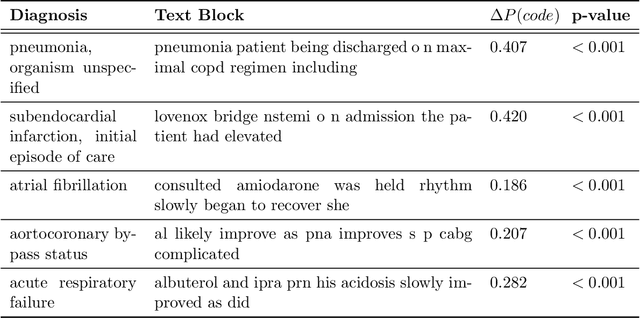
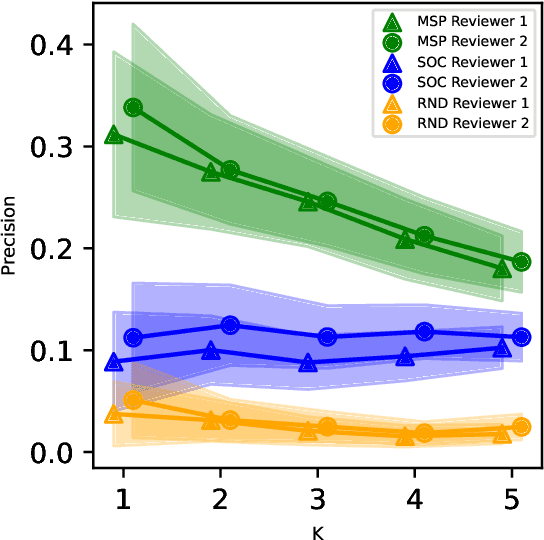
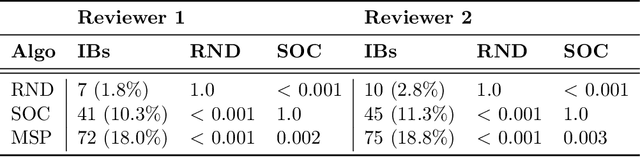
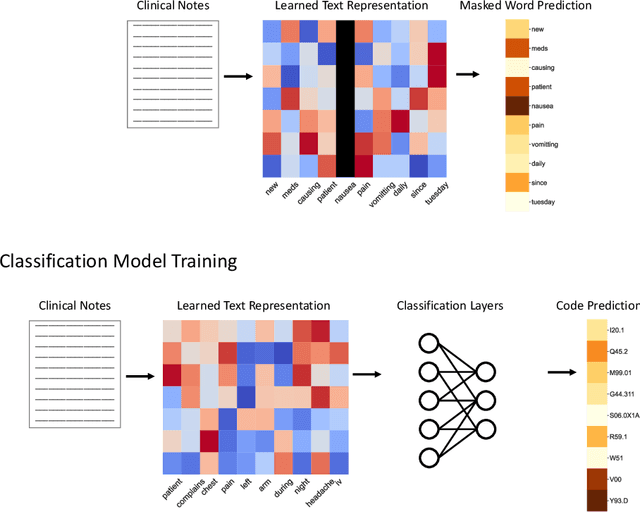
While Transformer language models (LMs) are state-of-the-art for information extraction, long text introduces computational challenges requiring suboptimal preprocessing steps or alternative model architectures. Sparse-attention LMs can represent longer sequences, overcoming performance hurdles. However, it remains unclear how to explain predictions from these models, as not all tokens attend to each other in the self-attention layers, and long sequences pose computational challenges for explainability algorithms when runtime depends on document length. These challenges are severe in the medical context where documents can be very long, and machine learning (ML) models must be auditable and trustworthy. We introduce a novel Masked Sampling Procedure (MSP) to identify the text blocks that contribute to a prediction, apply MSP in the context of predicting diagnoses from medical text, and validate our approach with a blind review by two clinicians. Our method identifies about 1.7x more clinically informative text blocks than the previous state-of-the-art, runs up to 100x faster, and is tractable for generating important phrase pairs. MSP is particularly well-suited to long LMs but can be applied to any text classifier. We provide a general implementation of MSP.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge