Explainable Severity ranking via pairwise n-hidden comparison: a case study of glaucoma
Paper and Code
Dec 05, 2023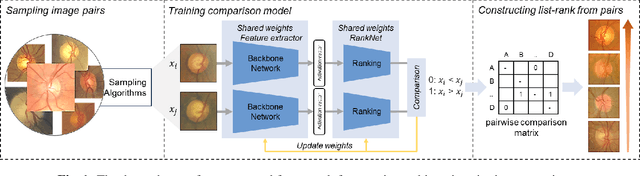
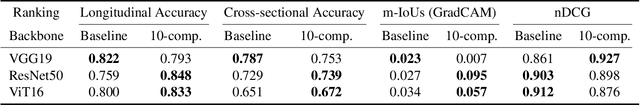
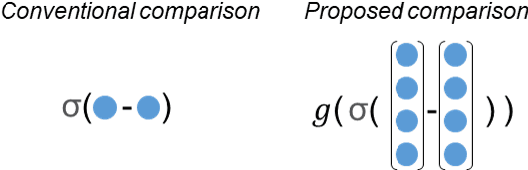
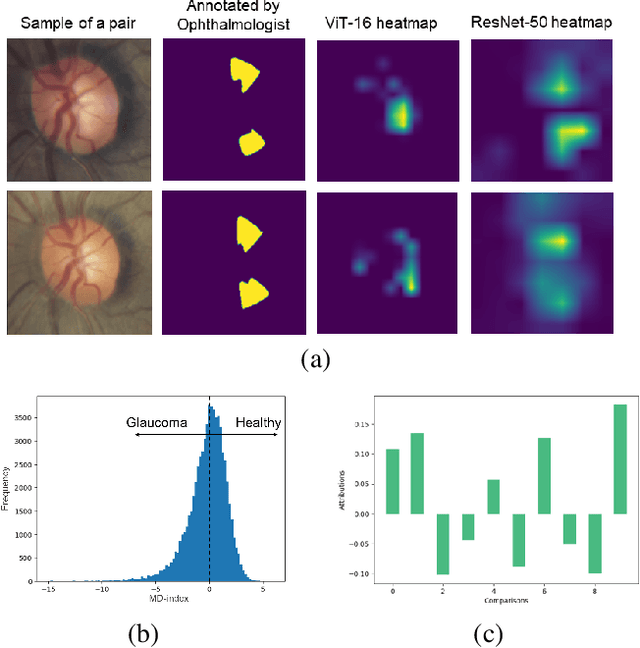
Primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG) is a chronic and progressive optic nerve condition that results in an acquired loss of optic nerve fibers and potential blindness. The gradual onset of glaucoma results in patients progressively losing their vision without being consciously aware of the changes. To diagnose POAG and determine its severity, patients must undergo a comprehensive dilated eye examination. In this work, we build a framework to rank, compare, and interpret the severity of glaucoma using fundus images. We introduce a siamese-based severity ranking using pairwise n-hidden comparisons. We additionally have a novel approach to explaining why a specific image is deemed more severe than others. Our findings indicate that the proposed severity ranking model surpasses traditional ones in terms of diagnostic accuracy and delivers improved saliency explanations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge