Evolutionary Approach to Security Games with Signaling
Paper and Code
Apr 29, 2022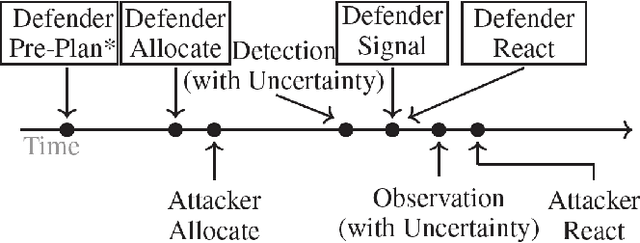
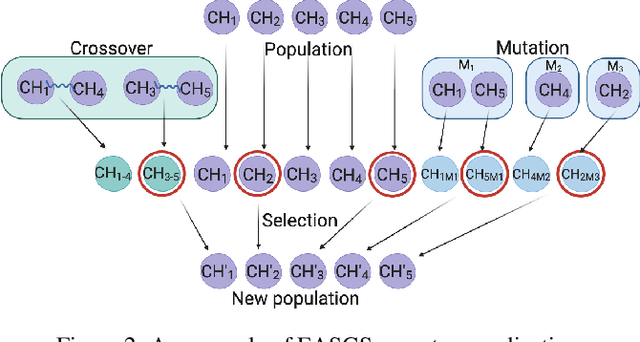
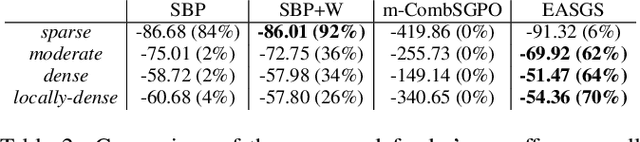
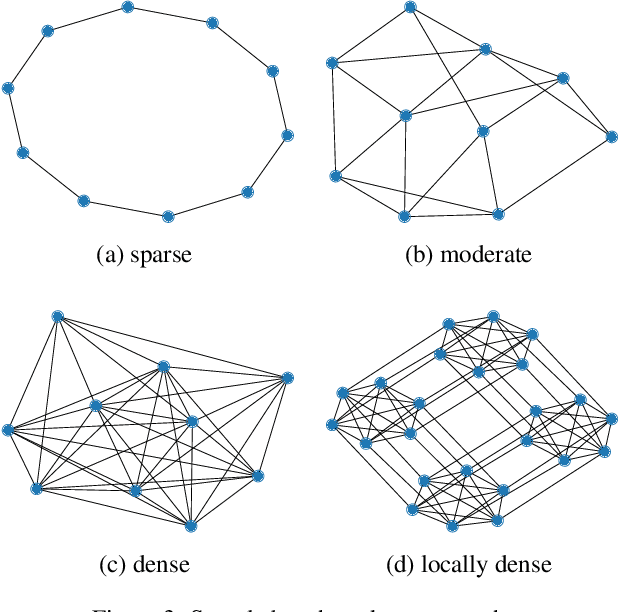
Green Security Games have become a popular way to model scenarios involving the protection of natural resources, such as wildlife. Sensors (e.g. drones equipped with cameras) have also begun to play a role in these scenarios by providing real-time information. Incorporating both human and sensor defender resources strategically is the subject of recent work on Security Games with Signaling (SGS). However, current methods to solve SGS do not scale well in terms of time or memory. We therefore propose a novel approach to SGS, which, for the first time in this domain, employs an Evolutionary Computation paradigm: EASGS. EASGS effectively searches the huge SGS solution space via suitable solution encoding in a chromosome and a specially-designed set of operators. The operators include three types of mutations, each focusing on a particular aspect of the SGS solution, optimized crossover and a local coverage improvement scheme (a memetic aspect of EASGS). We also introduce a new set of benchmark games, based on dense or locally-dense graphs that reflect real-world SGS settings. In the majority of 342 test game instances, EASGS outperforms state-of-the-art methods, including a reinforcement learning method, in terms of time scalability, nearly constant memory utilization, and quality of the returned defender's strategies (expected payoffs).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge