Evidential relational clustering using medoids
Paper and Code
Jul 15, 2015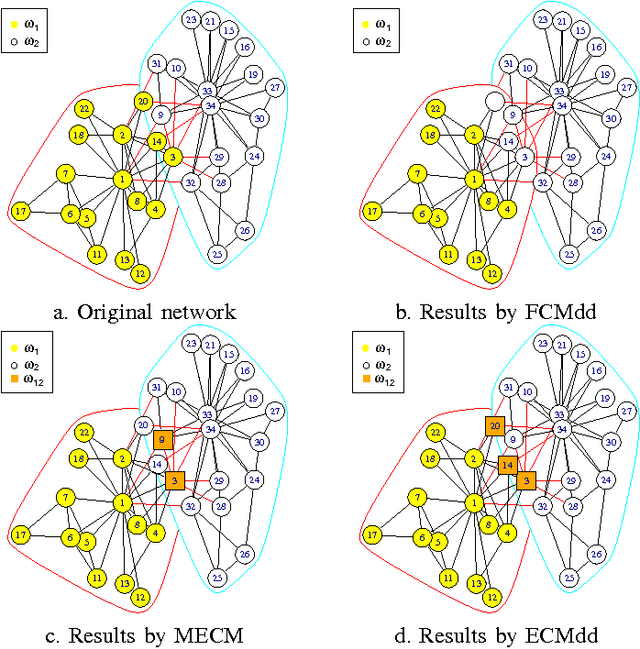
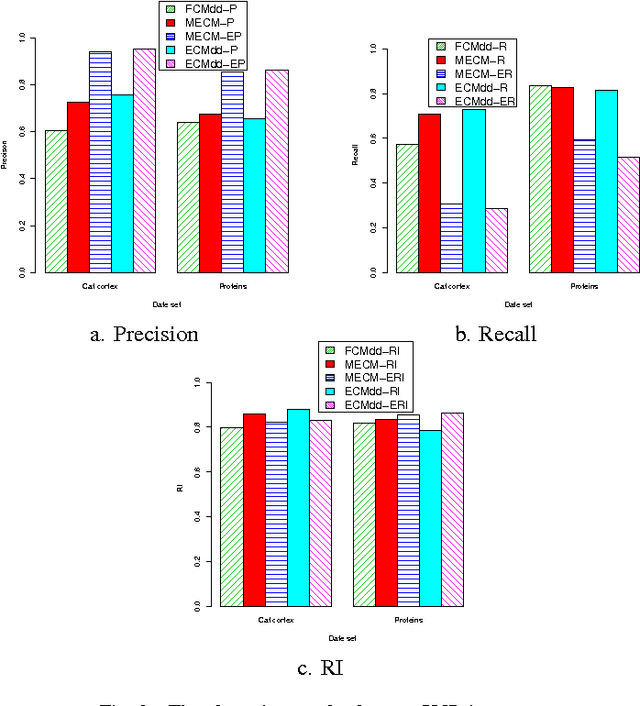
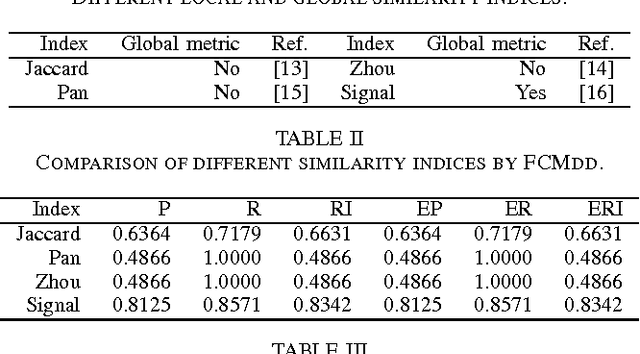
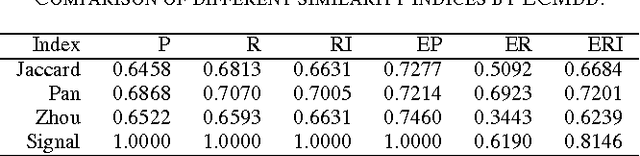
In real clustering applications, proximity data, in which only pairwise similarities or dissimilarities are known, is more general than object data, in which each pattern is described explicitly by a list of attributes. Medoid-based clustering algorithms, which assume the prototypes of classes are objects, are of great value for partitioning relational data sets. In this paper a new prototype-based clustering method, named Evidential C-Medoids (ECMdd), which is an extension of Fuzzy C-Medoids (FCMdd) on the theoretical framework of belief functions is proposed. In ECMdd, medoids are utilized as the prototypes to represent the detected classes, including specific classes and imprecise classes. Specific classes are for the data which are distinctly far from the prototypes of other classes, while imprecise classes accept the objects that may be close to the prototypes of more than one class. This soft decision mechanism could make the clustering results more cautious and reduce the misclassification rates. Experiments in synthetic and real data sets are used to illustrate the performance of ECMdd. The results show that ECMdd could capture well the uncertainty in the internal data structure. Moreover, it is more robust to the initializations compared with FCMdd.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge