Energy-Based Reranking: Improving Neural Machine Translation Using Energy-Based Models
Paper and Code
Sep 20, 2020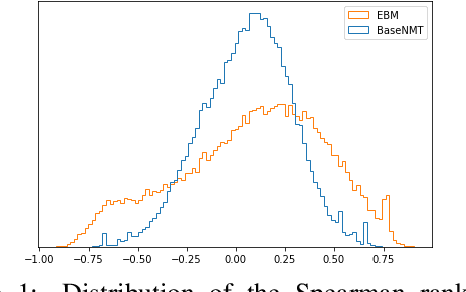
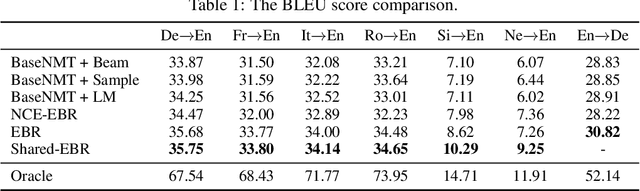
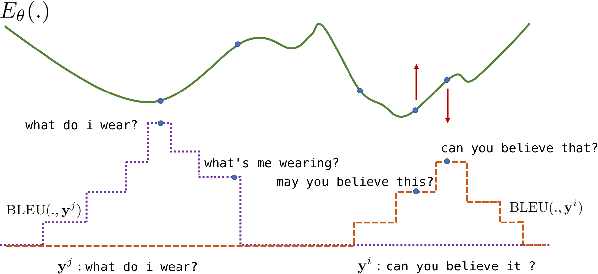
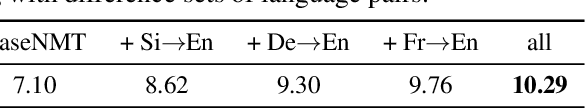
The discrepancy between maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) and task measures such as BLEU score has been studied before for autoregressive neural machine translation (NMT) and resulted in alternative training algorithms (Ranzato et al., 2016; Norouzi et al., 2016; Shen et al., 2016; Wu et al., 2018). However, MLE training remains the de facto approach for autoregressive NMT because of its computational efficiency and stability. Despite this mismatch between the training objective and task measure, we notice that the samples drawn from an MLE-based trained NMT support the desired distribution -- there are samples with much higher BLEU score comparing to the beam decoding output. To benefit from this observation, we train an energy-based model to mimic the behavior of the task measure (i.e., the energy-based model assigns lower energy to samples with higher BLEU score), which is resulted in a re-ranking algorithm based on the samples drawn from NMT: energy-based re-ranking (EBR). Our EBR consistently improves the performance of the Transformer-based NMT: +3 BLEU points on Sinhala-English and +2.0 BLEU points on IWSLT'17 French-English tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge