End-to-end Emotion-Cause Pair Extraction via Learning to Link
Paper and Code
Feb 25, 2020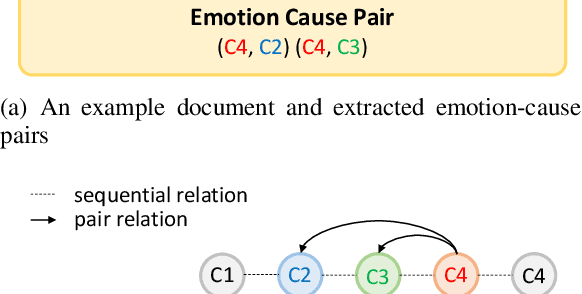
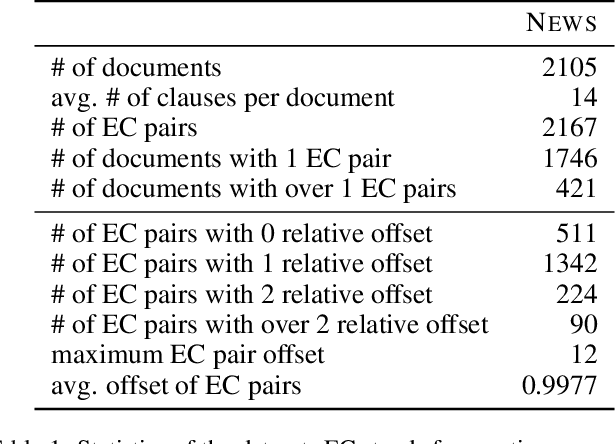
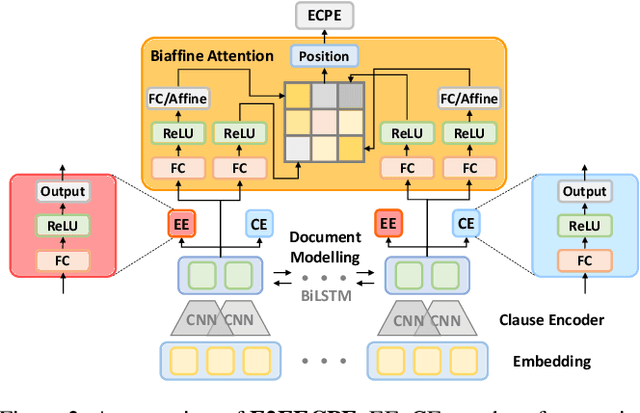
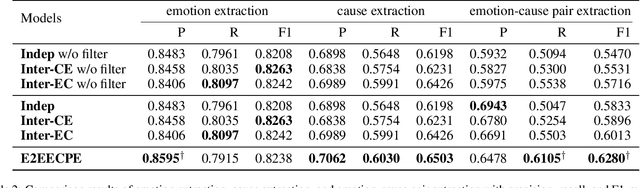
Emotion-cause pair extraction (ECPE), as an emergent natural language processing task, aims at jointly investigating emotions and their underlying causes in documents. It extends the previous emotion cause extraction (ECE) task, yet without requiring a set of pre-given emotion clauses as in ECE. Existing approaches to ECPE generally adopt a two-stage method, i.e., (1) emotion and cause detection, and then (2) pairing the detected emotions and causes. Such pipeline method, while intuitive, suffers from two critical issues, including error propagation across stages that may hinder the effectiveness, and high computational cost that would limit the practical application of the method. To tackle these issues, we propose a multi-task learning model that can extract emotions, causes and emotion-cause pairs simultaneously in an end-to-end manner. Specifically, our model regards pair extraction as a link prediction task, and learns to link from emotion clauses to cause clauses, i.e., the links are directional. Emotion extraction and cause extraction are incorporated into the model as auxiliary tasks, which further boost the pair extraction. Experiments are conducted on an ECPE benchmarking dataset. The results show that our proposed model outperforms a range of state-of-the-art approaches in terms of both effectiveness and efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge