ELAA Near-Field Localization and Sensing with Partial Blockage Detection
Paper and Code
Feb 24, 2024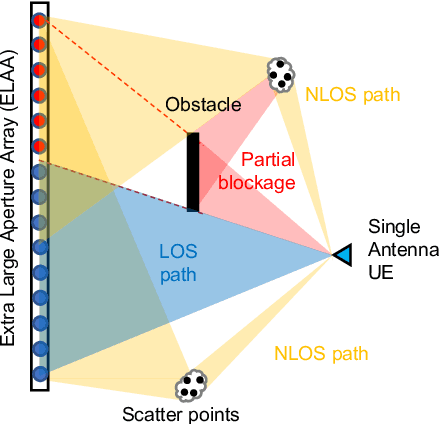
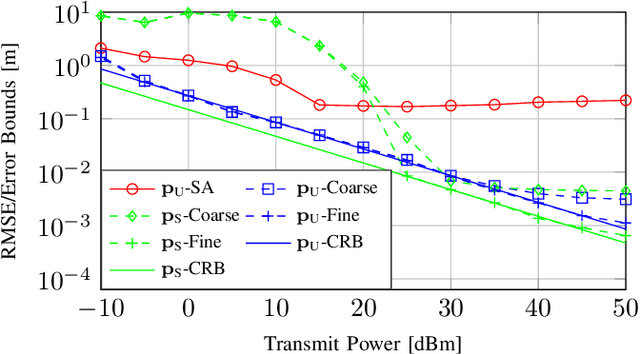
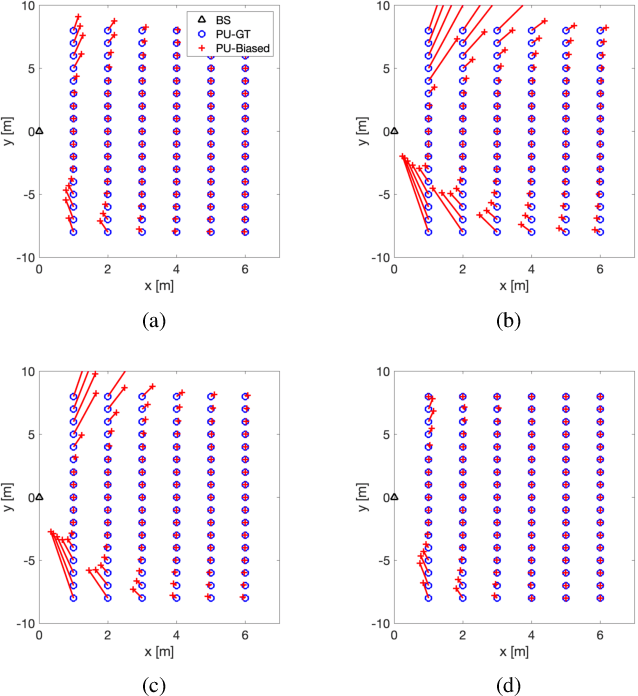
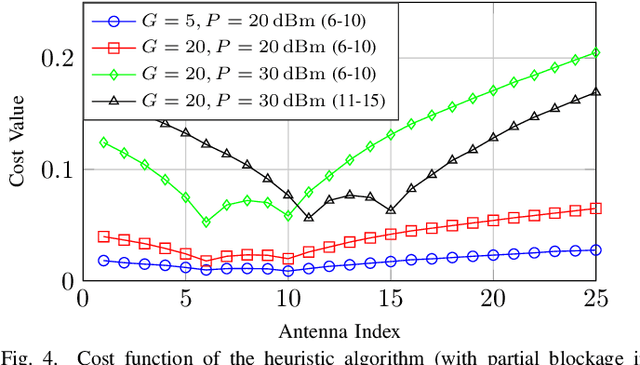
High-frequency communication systems bring extremely large aperture arrays (ELAA) and large bandwidths, integrating localization and (bi-static) sensing functions without extra infrastructure. Such systems are likely to operate in the near-field (NF), where the performance of localization and sensing is degraded if a simplified far-field channel model is considered. However, when taking advantage of the additional geometry information in the NF, e.g., the encapsulated information in the wavefront, localization and sensing performance can be improved. In this work, we formulate a joint synchronization, localization, and sensing problem in the NF. Considering the array size could be much larger than an obstacle, the effect of partial blockage (i.e., a portion of antennas are blocked) is investigated, and a blockage detection algorithm is proposed. The simulation results show that blockage greatly impacts performance for certain positions, and the proposed blockage detection algorithm can mitigate this impact by identifying the blocked antennas.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge