EEG-based Drowsiness Estimation for Driving Safety using Deep Q-Learning
Paper and Code
Jan 08, 2020
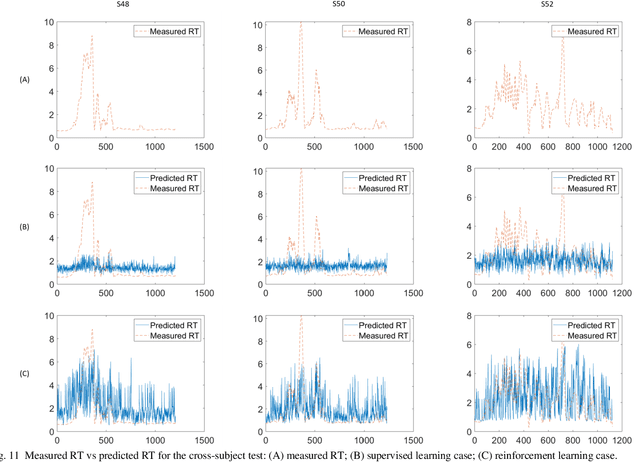
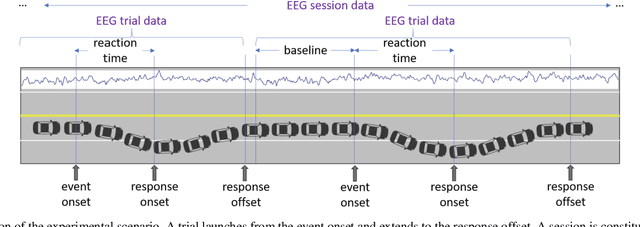
Fatigue is the most vital factor of road fatalities and one manifestation of fatigue during driving is drowsiness. In this paper, we propose using deep Q-learning to analyze an electroencephalogram (EEG) dataset captured during a simulated endurance driving test. By measuring the correlation between drowsiness and driving performance, this experiment represents an important brain-computer interface (BCI) paradigm especially from an application perspective. We adapt the terminologies in the driving test to fit the reinforcement learning framework, thus formulate the drowsiness estimation problem as an optimization of a Q-learning task. By referring to the latest deep Q-Learning technologies and attending to the characteristics of EEG data, we tailor a deep Q-network for action proposition that can indirectly estimate drowsiness. Our results show that the trained model can trace the variations of mind state in a satisfactory way against the testing EEG data, which demonstrates the feasibility and practicability of this new computation paradigm. We also show that our method outperforms the supervised learning counterpart and is superior for real applications. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to introduce the deep reinforcement learning method to this BCI scenario, and our method can be potentially generalized to other BCI cases.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge