Echocardiography Segmentation with Enforced Temporal Consistency
Paper and Code
Dec 03, 2021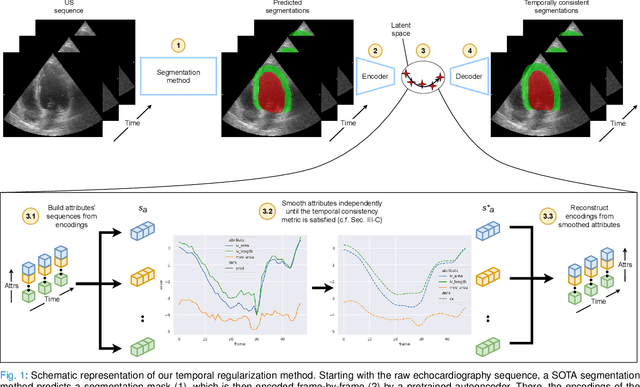
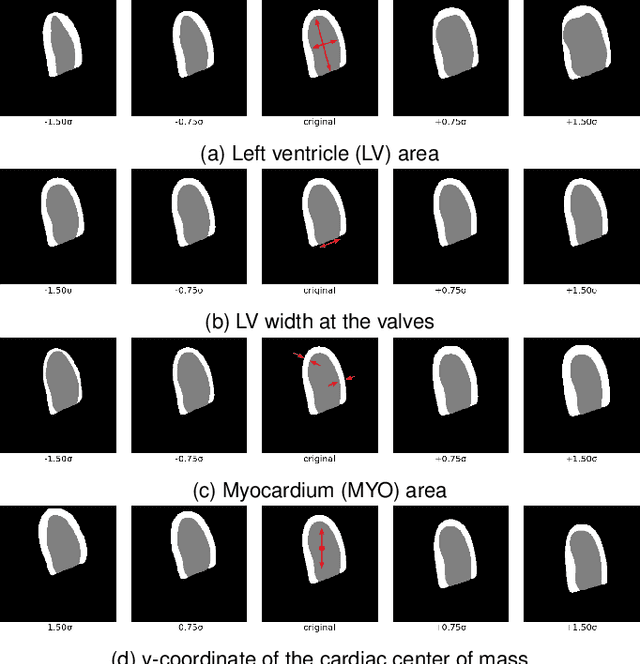
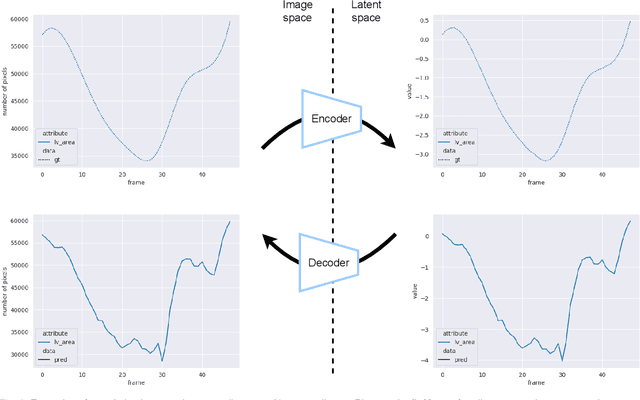

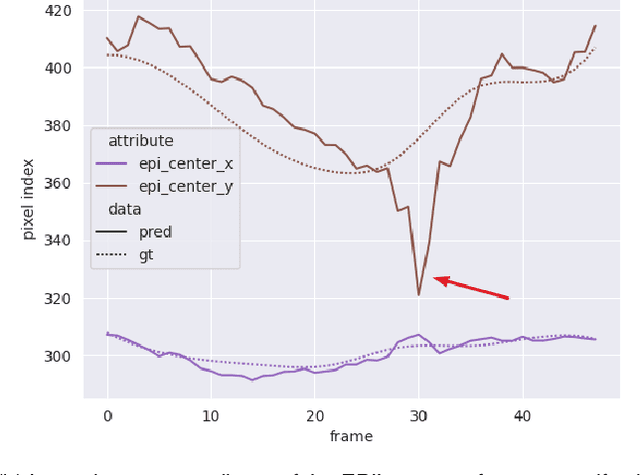
Convolutional neural networks (CNN) have demonstrated their ability to segment 2D cardiac ultrasound images. However, despite recent successes according to which the intra-observer variability on end-diastole and end-systole images has been reached, CNNs still struggle to leverage temporal information to provide accurate and temporally consistent segmentation maps across the whole cycle. Such consistency is required to accurately describe the cardiac function, a necessary step in diagnosing many cardiovascular diseases. In this paper, we propose a framework to learn the 2D+time long-axis cardiac shape such that the segmented sequences can benefit from temporal and anatomical consistency constraints. Our method is a post-processing that takes as input segmented echocardiographic sequences produced by any state-of-the-art method and processes it in two steps to (i) identify spatio-temporal inconsistencies according to the overall dynamics of the cardiac sequence and (ii) correct the inconsistencies. The identification and correction of cardiac inconsistencies relies on a constrained autoencoder trained to learn a physiologically interpretable embedding of cardiac shapes, where we can both detect and fix anomalies. We tested our framework on 98 full-cycle sequences from the CAMUS dataset, which will be rendered public alongside this paper. Our temporal regularization method not only improves the accuracy of the segmentation across the whole sequences, but also enforces temporal and anatomical consistency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge