Earlier Isn't Always Better: Sub-aspect Analysis on Corpus and System Biases in Summarization
Paper and Code
Aug 30, 2019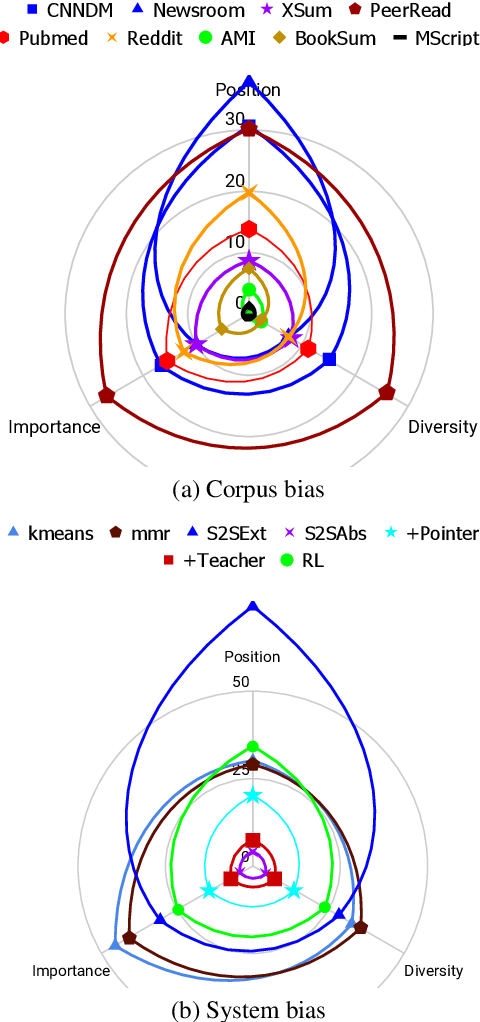

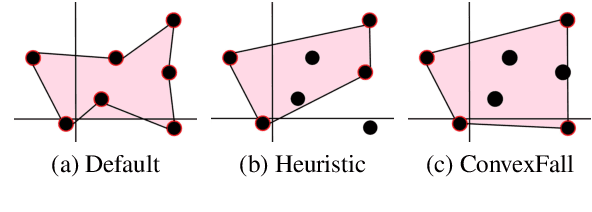
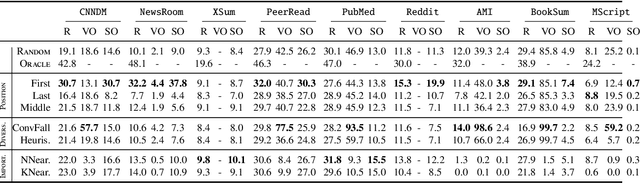
Despite the recent developments on neural summarization systems, the underlying logic behind the improvements from the systems and its corpus-dependency remains largely unexplored. Position of sentences in the original text, for example, is a well known bias for news summarization. Following in the spirit of the claim that summarization is a combination of sub-functions, we define three sub-aspects of summarization: position, importance, and diversity and conduct an extensive analysis of the biases of each sub-aspect with respect to the domain of nine different summarization corpora (e.g., news, academic papers, meeting minutes, movie script, books, posts). We find that while position exhibits substantial bias in news articles, this is not the case, for example, with academic papers and meeting minutes. Furthermore, our empirical study shows that different types of summarization systems (e.g., neural-based) are composed of different degrees of the sub-aspects. Our study provides useful lessons regarding consideration of underlying sub-aspects when collecting a new summarization dataset or developing a new system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge