Dual Skew Divergence Loss for Neural Machine Translation
Paper and Code
Aug 22, 2019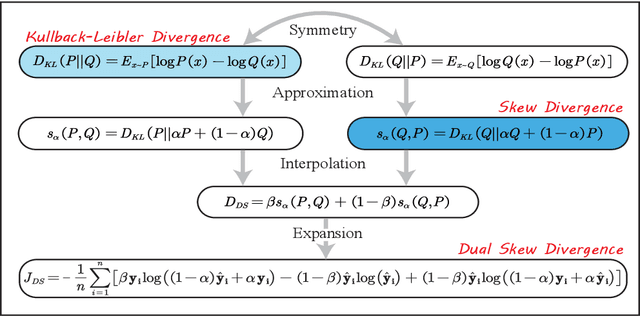
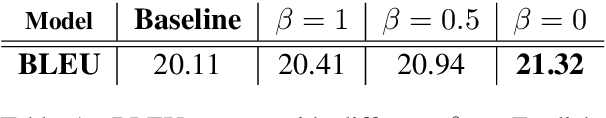
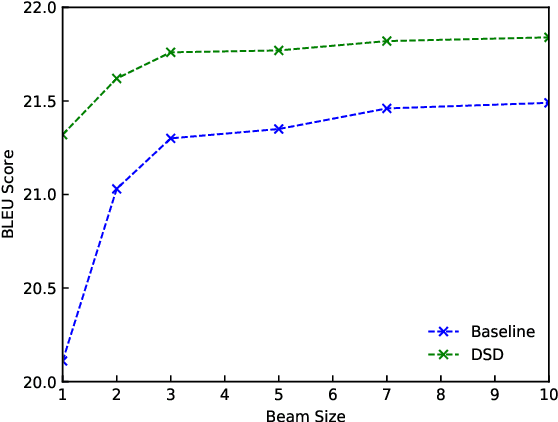
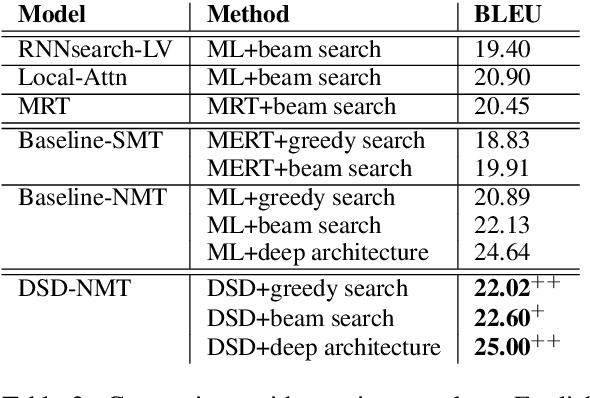
For neural sequence model training, maximum likelihood (ML) has been commonly adopted to optimize model parameters with respect to the corresponding objective. However, in the case of sequence prediction tasks like neural machine translation (NMT), training with the ML-based cross entropy loss would often lead to models that overgeneralize and plunge into local optima. In this paper, we propose an extended loss function called dual skew divergence (DSD), which aims to give a better tradeoff between generalization ability and error avoidance during NMT training. Our empirical study indicates that switching to DSD loss after the convergence of ML training helps the model skip the local optimum and stimulates a stable performance improvement. The evaluations on WMT 2014 English-German and English-French translation tasks demonstrate that the proposed loss indeed helps bring about better translation performance than several baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge