Domain Generalisation via Imprecise Learning
Paper and Code
Apr 06, 2024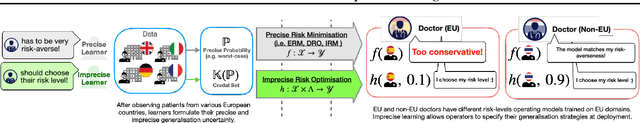
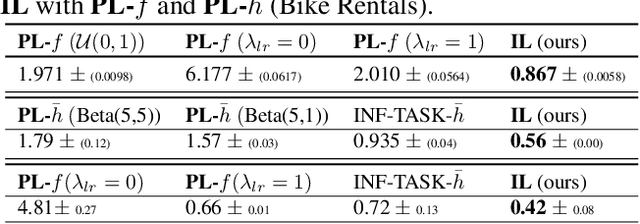
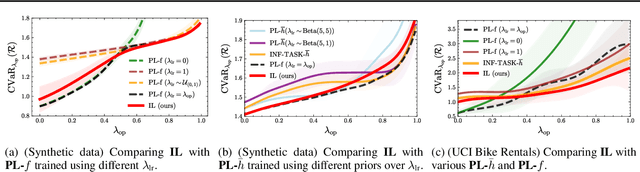
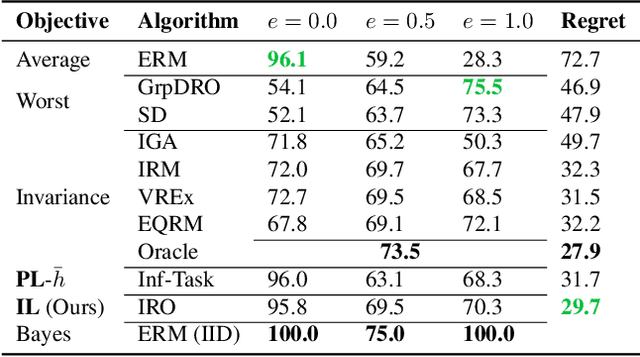
Out-of-distribution (OOD) generalisation is challenging because it involves not only learning from empirical data, but also deciding among various notions of generalisation, e.g., optimising the average-case risk, worst-case risk, or interpolations thereof. While this choice should in principle be made by the model operator like medical doctors, this information might not always be available at training time. The institutional separation between machine learners and model operators leads to arbitrary commitments to specific generalisation strategies by machine learners due to these deployment uncertainties. We introduce the Imprecise Domain Generalisation framework to mitigate this, featuring an imprecise risk optimisation that allows learners to stay imprecise by optimising against a continuous spectrum of generalisation strategies during training, and a model framework that allows operators to specify their generalisation preference at deployment. Supported by both theoretical and empirical evidence, our work showcases the benefits of integrating imprecision into domain generalisation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge