Does the Definition of Difficulty Matter? Scoring Functions and their Role for Curriculum Learning
Paper and Code
Nov 01, 2024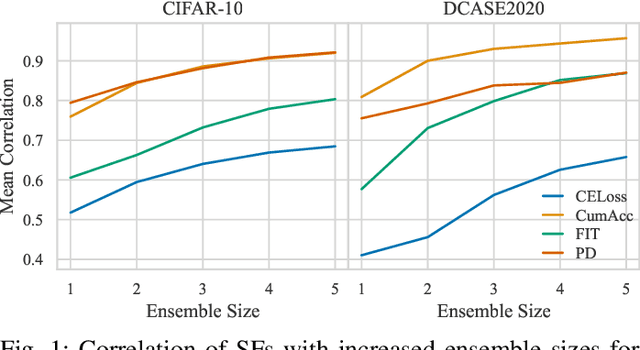
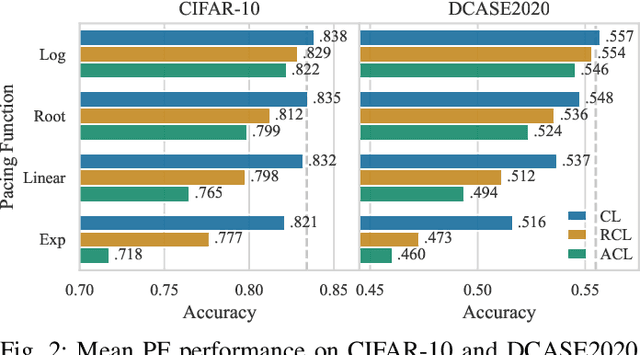
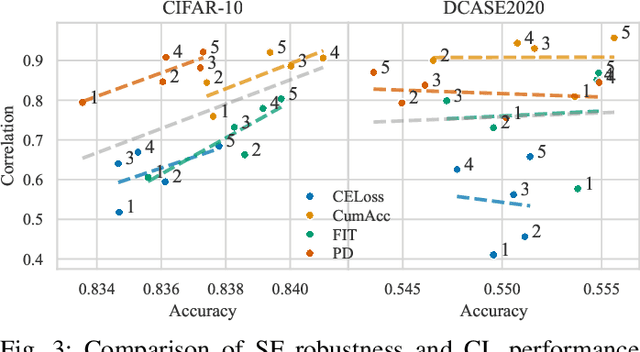
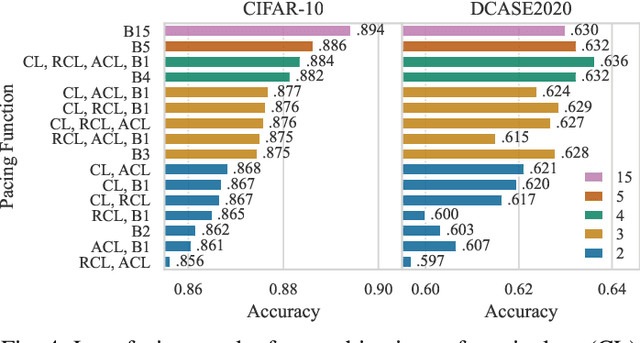
Curriculum learning (CL) describes a machine learning training strategy in which samples are gradually introduced into the training process based on their difficulty. Despite a partially contradictory body of evidence in the literature, CL finds popularity in deep learning research due to its promise of leveraging human-inspired curricula to achieve higher model performance. Yet, the subjectivity and biases that follow any necessary definition of difficulty, especially for those found in orderings derived from models or training statistics, have rarely been investigated. To shed more light on the underlying unanswered questions, we conduct an extensive study on the robustness and similarity of the most common scoring functions for sample difficulty estimation, as well as their potential benefits in CL, using the popular benchmark dataset CIFAR-10 and the acoustic scene classification task from the DCASE2020 challenge as representatives of computer vision and computer audition, respectively. We report a strong dependence of scoring functions on the training setting, including randomness, which can partly be mitigated through ensemble scoring. While we do not find a general advantage of CL over uniform sampling, we observe that the ordering in which data is presented for CL-based training plays an important role in model performance. Furthermore, we find that the robustness of scoring functions across random seeds positively correlates with CL performance. Finally, we uncover that models trained with different CL strategies complement each other by boosting predictive power through late fusion, likely due to differences in the learnt concepts. Alongside our findings, we release the aucurriculum toolkit (https://github.com/autrainer/aucurriculum), implementing sample difficulty and CL-based training in a modular fashion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge