Distill and De-bias: Mitigating Bias in Face Recognition using Knowledge Distillation
Paper and Code
Dec 17, 2021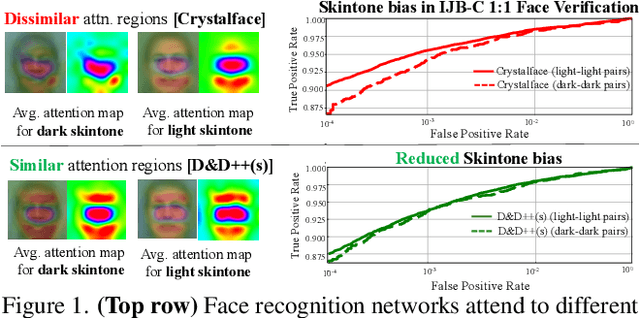
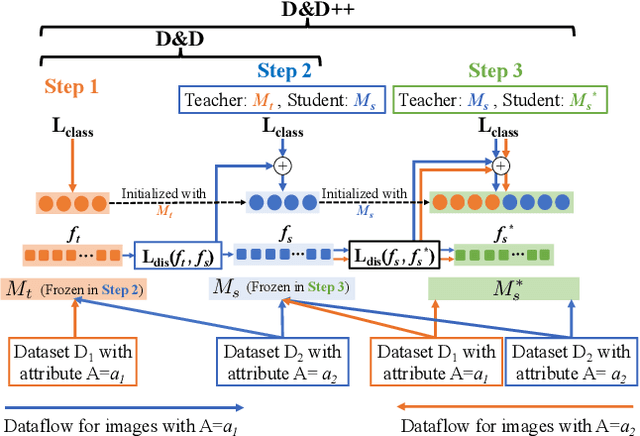
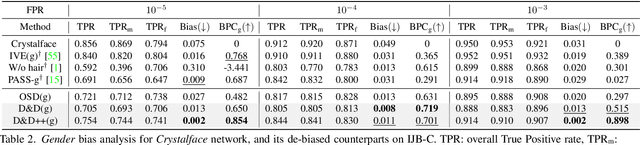
Face recognition networks generally demonstrate bias with respect to sensitive attributes like gender, skintone etc. For gender and skintone, we observe that the regions of the face that a network attends to vary by the category of an attribute. This might contribute to bias. Building on this intuition, we propose a novel distillation-based approach called Distill and De-bias (D&D) to enforce a network to attend to similar face regions, irrespective of the attribute category. In D&D, we train a teacher network on images from one category of an attribute; e.g. light skintone. Then distilling information from the teacher, we train a student network on images of the remaining category; e.g., dark skintone. A feature-level distillation loss constrains the student network to generate teacher-like representations. This allows the student network to attend to similar face regions for all attribute categories and enables it to reduce bias. We also propose a second distillation step on top of D&D, called D&D++. For the D&D++ network, we distill the `un-biasedness' of the D&D network into a new student network, the D&D++ network. We train the new network on all attribute categories; e.g., both light and dark skintones. This helps us train a network that is less biased for an attribute, while obtaining higher face verification performance than D&D. We show that D&D++ outperforms existing baselines in reducing gender and skintone bias on the IJB-C dataset, while obtaining higher face verification performance than existing adversarial de-biasing methods. We evaluate the effectiveness of our proposed methods on two state-of-the-art face recognition networks: Crystalface and ArcFace.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge