Disentangling Abstraction from Statistical Pattern Matching in Human and Machine Learning
Paper and Code
Apr 04, 2022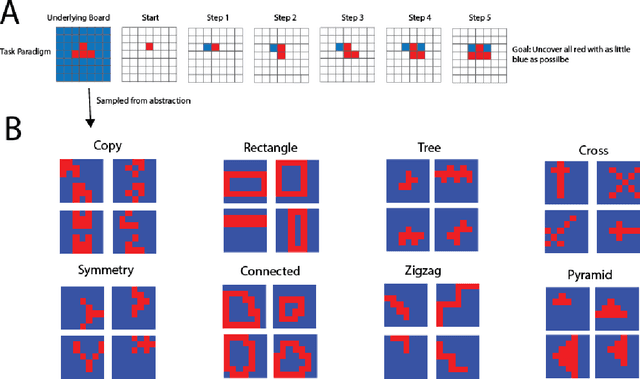
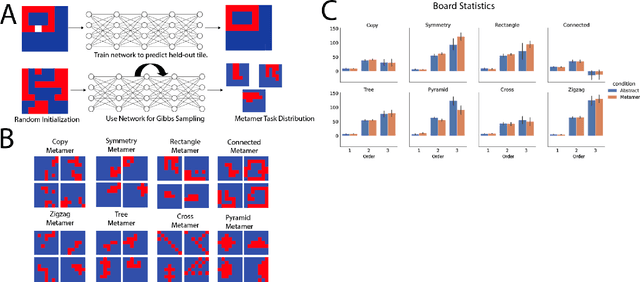
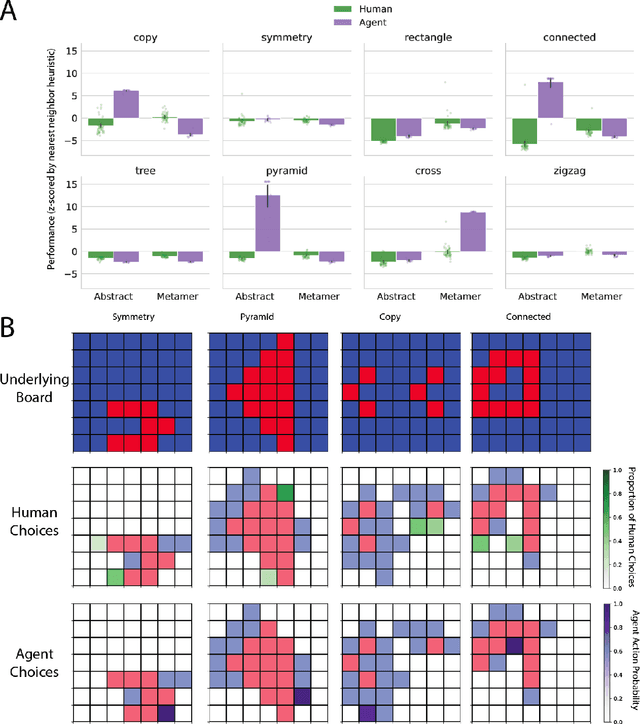
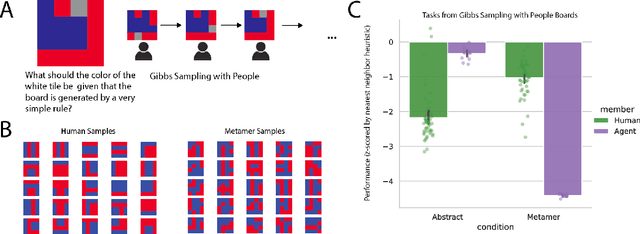
The ability to acquire abstract knowledge is a hallmark of human intelligence and is believed by many to be one of the core differences between humans and neural network models. Agents can be endowed with an inductive bias towards abstraction through meta-learning, where they are trained on a distribution of tasks that share some abstract structure that can be learned and applied. However, because neural networks are hard to interpret, it can be difficult to tell whether agents have learned the underlying abstraction, or alternatively statistical patterns that are characteristic of that abstraction. In this work, we compare the performance of humans and agents in a meta-reinforcement learning paradigm in which tasks are generated from abstract rules. We define a novel methodology for building "task metamers" that closely match the statistics of the abstract tasks but use a different underlying generative process, and evaluate performance on both abstract and metamer tasks. In our first set of experiments, we found that humans perform better at abstract tasks than metamer tasks whereas a widely-used meta-reinforcement learning agent performs worse on the abstract tasks than the matched metamers. In a second set of experiments, we base the tasks on abstractions derived directly from empirically identified human priors. We utilize the same procedure to generate corresponding metamer tasks, and see the same double dissociation between humans and agents. This work provides a foundation for characterizing differences between humans and machine learning that can be used in future work towards developing machines with human-like behavior.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge