Discovering Sensorimotor Agency in Cellular Automata using Diversity Search
Paper and Code
Feb 14, 2024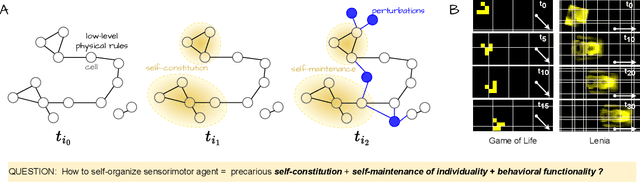
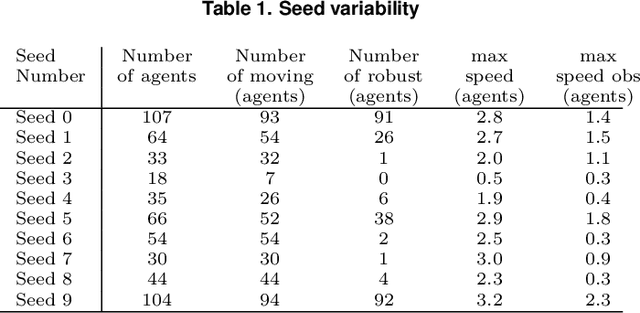
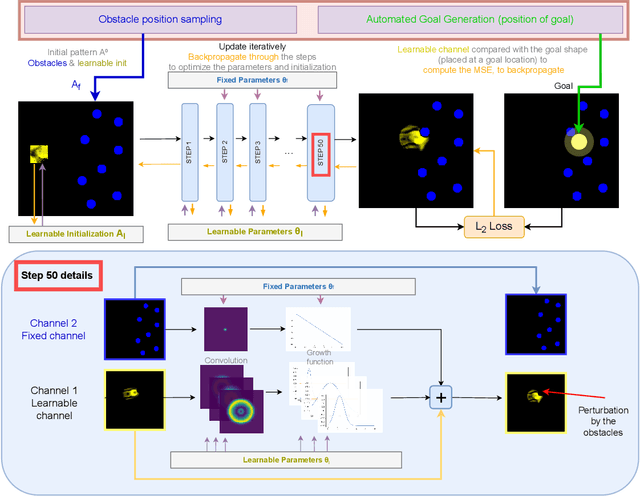
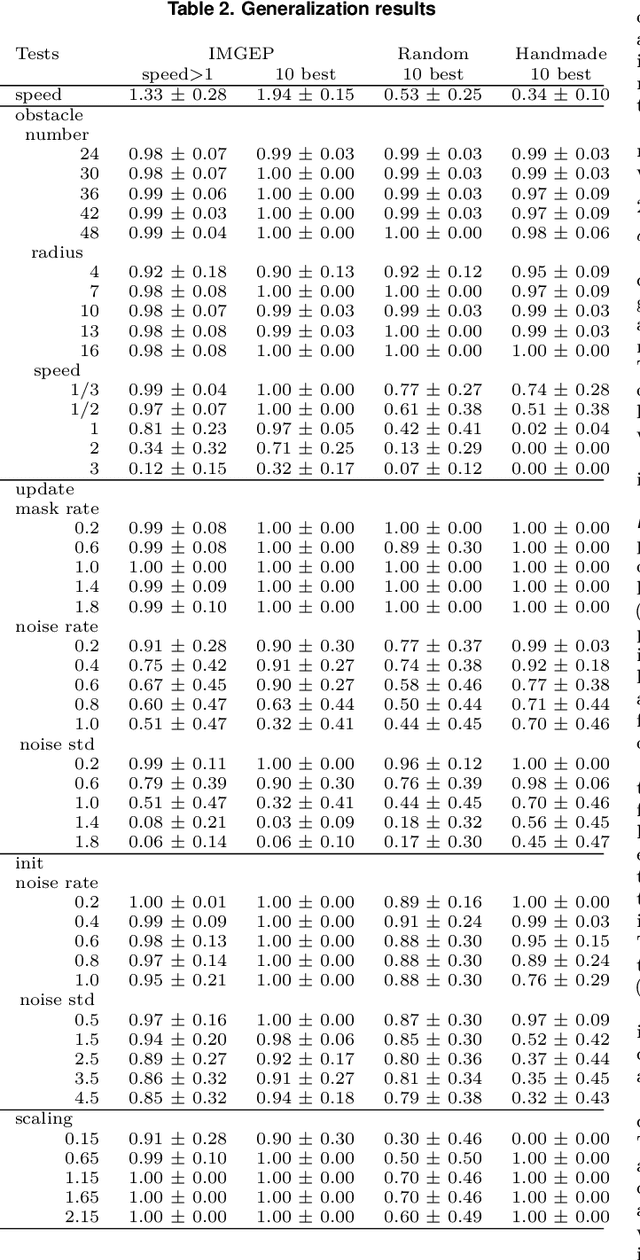
The research field of Artificial Life studies how life-like phenomena such as autopoiesis, agency, or self-regulation can self-organize in computer simulations. In cellular automata (CA), a key open-question has been whether it it is possible to find environment rules that self-organize robust "individuals" from an initial state with no prior existence of things like "bodies", "brain", "perception" or "action". In this paper, we leverage recent advances in machine learning, combining algorithms for diversity search, curriculum learning and gradient descent, to automate the search of such "individuals", i.e. localized structures that move around with the ability to react in a coherent manner to external obstacles and maintain their integrity, hence primitive forms of sensorimotor agency. We show that this approach enables to find systematically environmental conditions in CA leading to self-organization of such basic forms of agency. Through multiple experiments, we show that the discovered agents have surprisingly robust capabilities to move, maintain their body integrity and navigate among various obstacles. They also show strong generalization abilities, with robustness to changes of scale, random updates or perturbations from the environment not seen during training. We discuss how this approach opens new perspectives in AI and synthetic bioengineering.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge