Disambiguation of One-Shot Visual Classification Tasks: A Simplex-Based Approach
Paper and Code
Jan 16, 2023
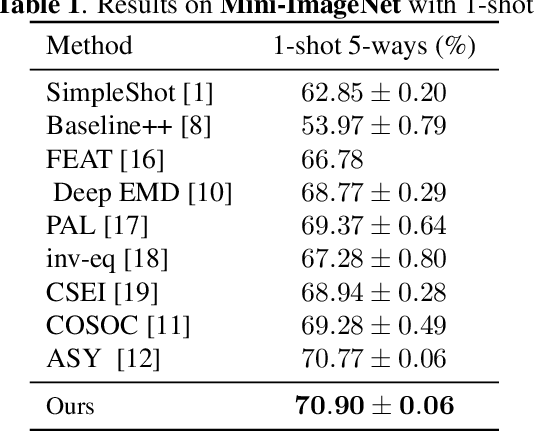
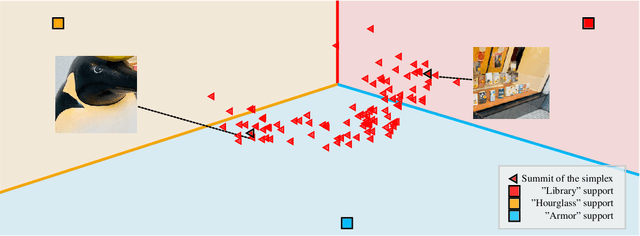

The field of visual few-shot classification aims at transferring the state-of-the-art performance of deep learning visual systems onto tasks where only a very limited number of training samples are available. The main solution consists in training a feature extractor using a large and diverse dataset to be applied to the considered few-shot task. Thanks to the encoded priors in the feature extractors, classification tasks with as little as one example (or "shot'') for each class can be solved with high accuracy, even when the shots display individual features not representative of their classes. Yet, the problem becomes more complicated when some of the given shots display multiple objects. In this paper, we present a strategy which aims at detecting the presence of multiple and previously unseen objects in a given shot. This methodology is based on identifying the corners of a simplex in a high dimensional space. We introduce an optimization routine and showcase its ability to successfully detect multiple (previously unseen) objects in raw images. Then, we introduce a downstream classifier meant to exploit the presence of multiple objects to improve the performance of few-shot classification, in the case of extreme settings where only one shot is given for its class. Using standard benchmarks of the field, we show the ability of the proposed method to slightly, yet statistically significantly, improve accuracy in these settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge