Direct and Real-Time Cardiovascular Risk Prediction
Paper and Code
Dec 08, 2017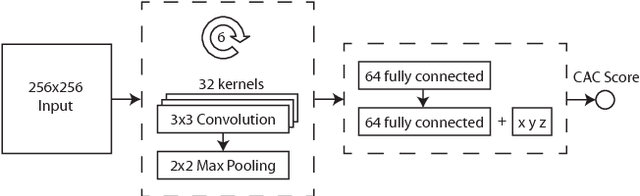
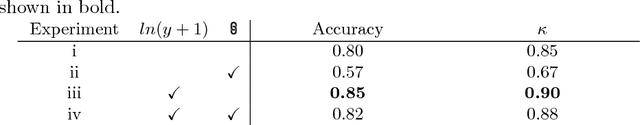
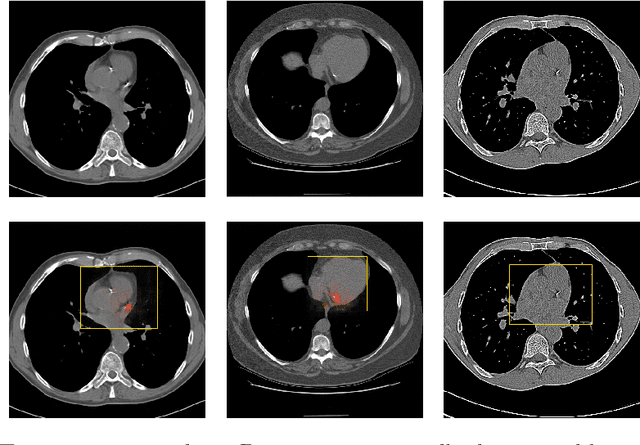
Coronary artery calcium (CAC) burden quantified in low-dose chest CT is a predictor of cardiovascular events. We propose an automatic method for CAC quantification, circumventing intermediate segmentation of CAC. The method determines a bounding box around the heart using a ConvNet for localization. Subsequently, a dedicated ConvNet analyzes axial slices within the bounding boxes to determine CAC quantity by regression. A dataset of 1,546 baseline CT scans was used from the National Lung Screening Trial with manually identified CAC. The method achieved an ICC of 0.98 between manual reference and automatically obtained Agatston scores. Stratification of subjects into five cardiovascular risk categories resulted in an accuracy of 85\% and Cohen's linearly weighted $\kappa$ of 0.90. The results demonstrate that real-time quantification of CAC burden in chest CT without the need for segmentation of CAC is possible.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge