Dilated Continuous Random Field for Semantic Segmentation
Paper and Code
Feb 01, 2022

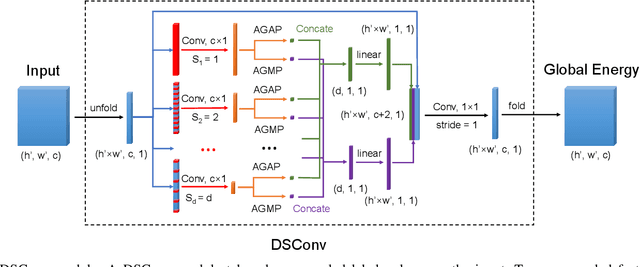
Mean field approximation methodology has laid the foundation of modern Continuous Random Field (CRF) based solutions for the refinement of semantic segmentation. In this paper, we propose to relax the hard constraint of mean field approximation - minimizing the energy term of each node from probabilistic graphical model, by a global optimization with the proposed dilated sparse convolution module (DSConv). In addition, adaptive global average-pooling and adaptive global max-pooling are implemented as replacements of fully connected layers. In order to integrate DSConv, we design an end-to-end, time-efficient DilatedCRF pipeline. The unary energy term is derived either from pre-softmax and post-softmax features, or the predicted affordance map using a conventional classifier, making it easier to implement DilatedCRF for varieties of classifiers. We also present superior experimental results of proposed approach on the suction dataset comparing to other CRF-based approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge