Differentiable Representations For Multihop Inference Rules
Paper and Code
May 24, 2019
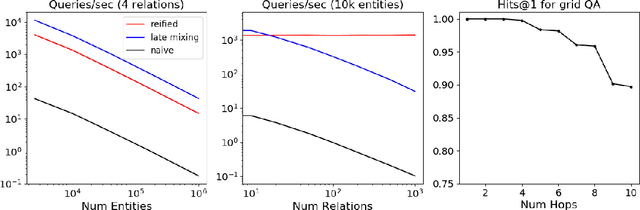
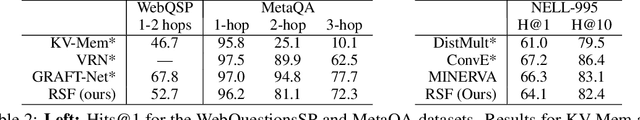
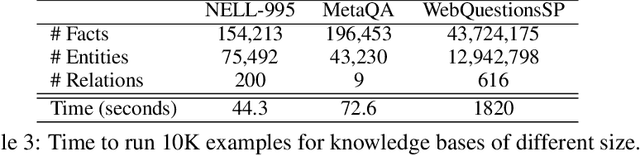
We present efficient differentiable implementations of second-order multi-hop reasoning using a large symbolic knowledge base (KB). We introduce a new operation which can be used to compositionally construct second-order multi-hop templates in a neural model, and evaluate a number of alternative implementations, with different time and memory trade offs. These techniques scale to KBs with millions of entities and tens of millions of triples, and lead to simple models with competitive performance on several learning tasks requiring multi-hop reasoning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge