Differentiable Rendering with Reparameterized Volume Sampling
Paper and Code
Feb 21, 2023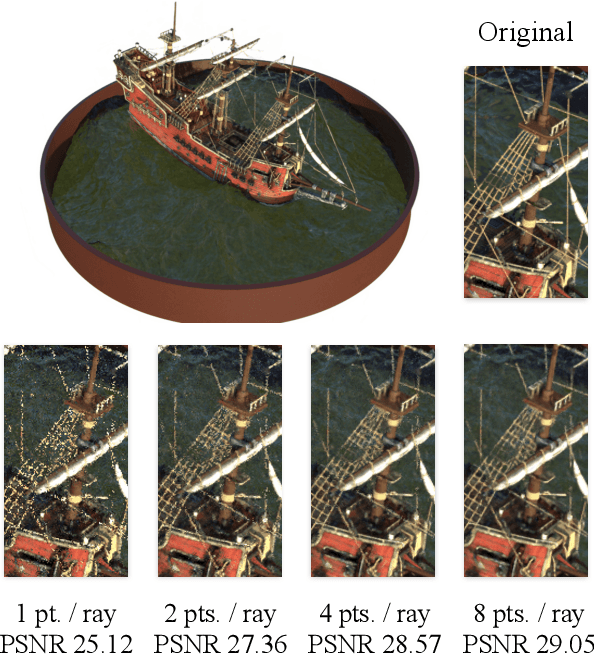
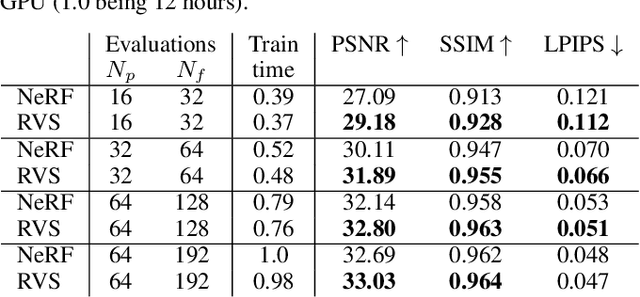
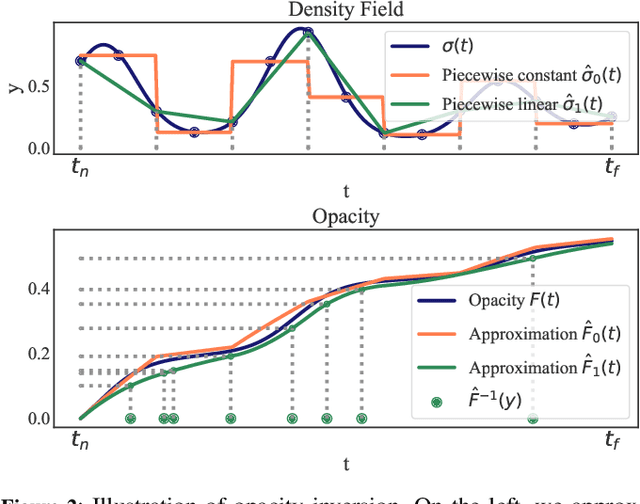
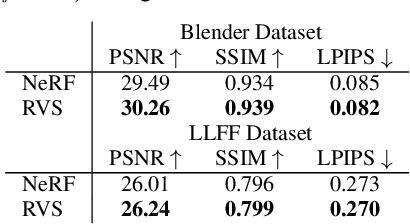
In view synthesis, a neural radiance field approximates underlying density and radiance fields based on a sparse set of scene pictures. To generate a pixel of a novel view, it marches a ray through the pixel and computes a weighted sum of radiance emitted from a dense set of ray points. This rendering algorithm is fully differentiable and facilitates gradient-based optimization of the fields. However, in practice, only a tiny opaque portion of the ray contributes most of the radiance to the sum. We propose an end-to-end differentiable sampling algorithm based on inverse transform sampling. It generates samples according to the probability distribution induced by the density field and picks non-transparent points on the ray. We utilize the algorithm in two ways. First, we propose a novel rendering approach based on Monte Carlo estimates. Such a rendering algorithm allows for optimizing a neural radiance field with just a few radiance field evaluations per ray. Second, we use the sampling algorithm to modify the hierarchical scheme used in the original work on neural radiance fields. In this setup, we were able to train the proposal network end-to-end without any auxiliary losses and improved the baseline performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge