Devil's in the Detail: Graph-based Key-point Alignment and Embedding for Person Re-ID
Paper and Code
Sep 11, 2020

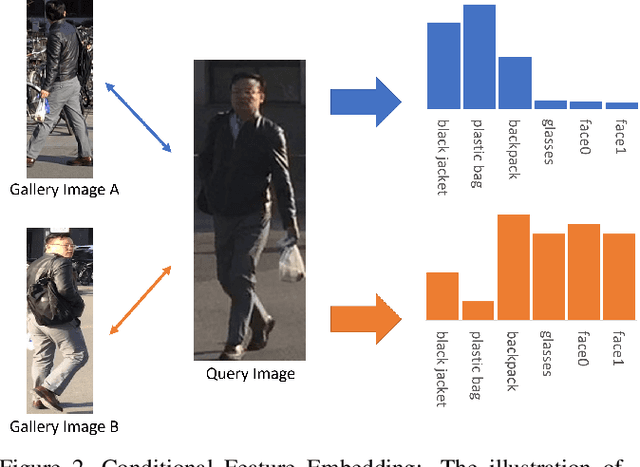
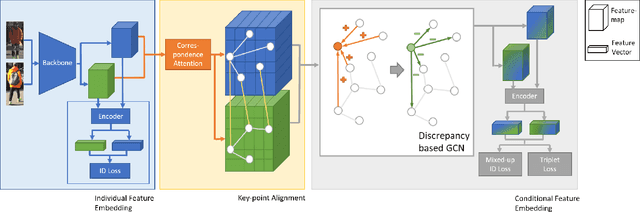
Although Person Re-Identification has made impressive progress, difficult cases like occlusion, change of view-point and similar clothing still bring great challenges. Besides overall visual features, matching and comparing detailed local information is also essential for tackling these challenges. This paper proposes two key recognition patterns to better utilize the local information of pedestrian images. From the spatial perspective, the model should be able to select and align key-points from the image pairs for comparison (i.e. key-points alignment). From the perspective of feature channels, the feature of a query image should be dynamically adjusted based on the gallery image it needs to match (i.e. conditional feature embedding). Most of the existing methods are unable to satisfy both key-point alignment and conditional feature embedding. By introducing novel techniques including correspondence attention module and discrepancy-based GCN, we propose an end-to-end ReID method that integrates both patterns into a unified framework, called Siamese-GCN. The experiments show that Siamese-GCN achieves state-of-the-art performance on three public datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge