Detecting Machine-Translated Paragraphs by Matching Similar Words
Paper and Code
Apr 24, 2019
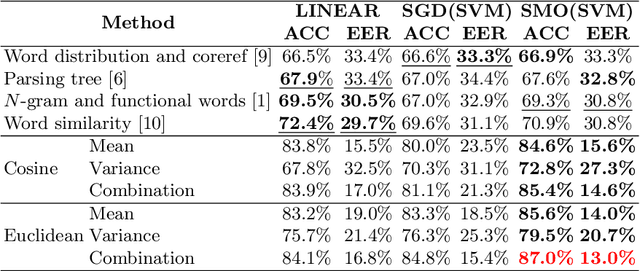
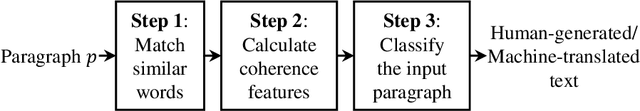
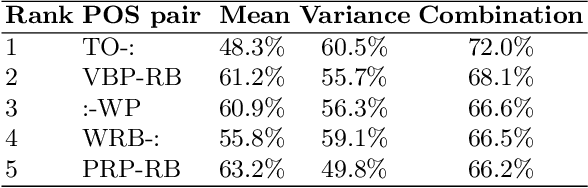
Machine-translated text plays an important role in modern life by smoothing communication from various communities using different languages. However, unnatural translation may lead to misunderstanding, a detector is thus needed to avoid the unfortunate mistakes. While a previous method measured the naturalness of continuous words using a N-gram language model, another method matched noncontinuous words across sentences but this method ignores such words in an individual sentence. We have developed a method matching similar words throughout the paragraph and estimating the paragraph-level coherence, that can identify machine-translated text. Experiment evaluates on 2000 English human-generated and 2000 English machine-translated paragraphs from German showing that the coherence-based method achieves high performance (accuracy = 87.0%; equal error rate = 13.0%). It is efficiently better than previous methods (best accuracy = 72.4%; equal error rate = 29.7%). Similar experiments on Dutch and Japanese obtain 89.2% and 97.9% accuracy, respectively. The results demonstrate the persistence of the proposed method in various languages with different resource levels.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge