Deformation Flow Based Two-Stream Network for Lip Reading
Paper and Code
Mar 13, 2020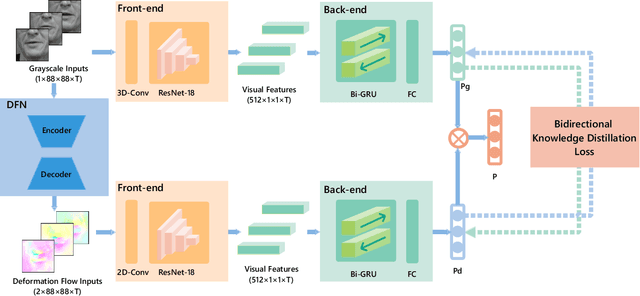
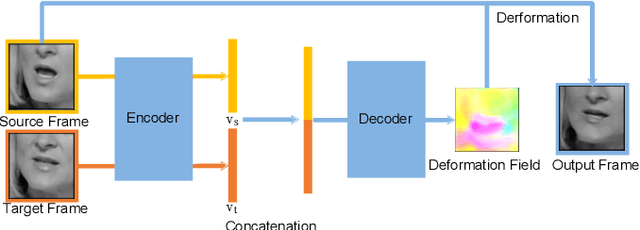

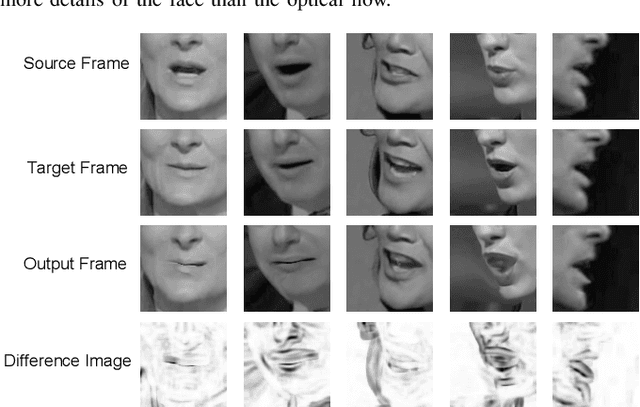
Lip reading is the task of recognizing the speech content by analyzing movements in the lip region when people are speaking. Observing on the continuity in adjacent frames in the speaking process, and the consistency of the motion patterns among different speakers when they pronounce the same phoneme, we model the lip movements in the speaking process as a sequence of apparent deformations in the lip region. Specifically, we introduce a Deformation Flow Network (DFN) to learn the deformation flow between adjacent frames, which directly captures the motion information within the lip region. The learned deformation flow is then combined with the original grayscale frames with a two-stream network to perform lip reading. Different from previous two-stream networks, we make the two streams learn from each other in the learning process by introducing a bidirectional knowledge distillation loss to train the two branches jointly. Owing to the complementary cues provided by different branches, the two-stream network shows a substantial improvement over using either single branch. A thorough experimental evaluation on two large-scale lip reading benchmarks is presented with detailed analysis. The results accord with our motivation, and show that our method achieves state-of-the-art or comparable performance on these two challenging datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge