DeepVIO: Self-supervised Deep Learning of Monocular Visual Inertial Odometry using 3D Geometric Constraints
Paper and Code
Jun 28, 2019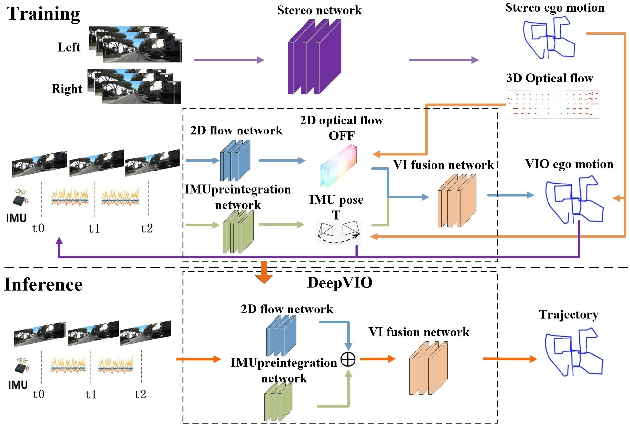
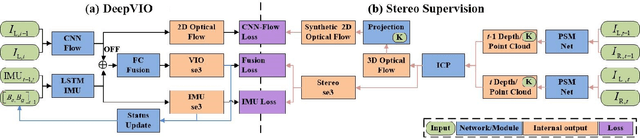
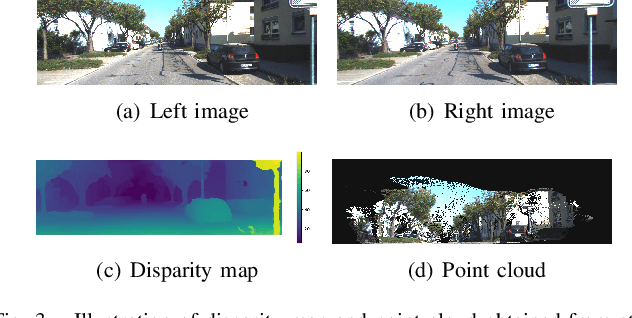
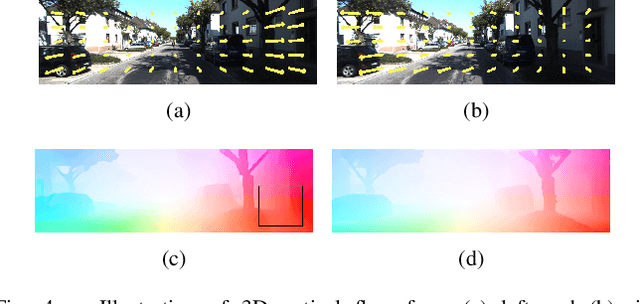
This paper presents an self-supervised deep learning network for monocular visual inertial odometry (named DeepVIO). DeepVIO provides absolute trajectory estimation by directly merging 2D optical flow feature (OFF) and Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU) data. Specifically, it firstly estimates the depth and dense 3D point cloud of each scene by using stereo sequences, and then obtains 3D geometric constraints including 3D optical flow and 6-DoF pose as supervisory signals. Note that such 3D optical flow shows robustness and accuracy to dynamic objects and textureless environments. In DeepVIO training, 2D optical flow network is constrained by the projection of its corresponding 3D optical flow, and LSTM-style IMU preintegration network and the fusion network are learned by minimizing the loss functions from ego-motion constraints. Furthermore, we employ an IMU status update scheme to improve IMU pose estimation through updating the additional gyroscope and accelerometer bias. The experimental results on KITTI and EuRoC datasets show that DeepVIO outperforms state-of-the-art learning based methods in terms of accuracy and data adaptability. Compared to the traditional methods, DeepVIO reduces the impacts of inaccurate Camera-IMU calibrations, unsynchronized and missing data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge