Deep Multimodal Image-Text Embeddings for Automatic Cross-Media Retrieval
Paper and Code
Feb 23, 2020
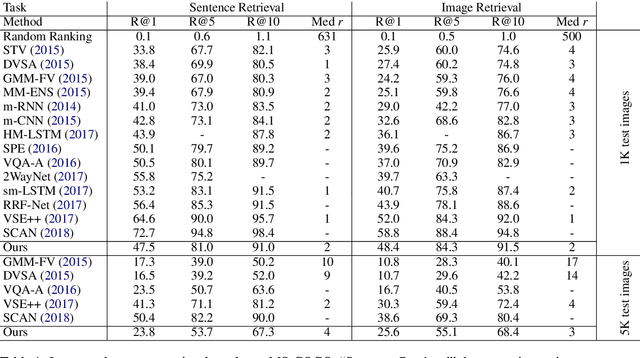
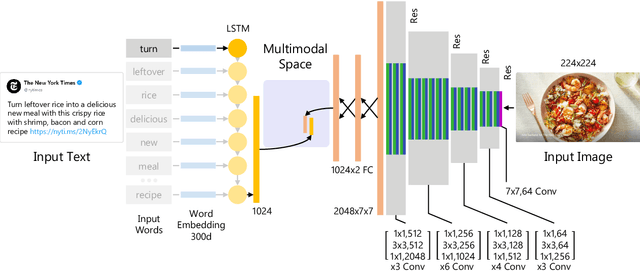
This paper considers the task of matching images and sentences by learning a visual-textual embedding space for cross-modal retrieval. Finding such a space is a challenging task since the features and representations of text and image are not comparable. In this work, we introduce an end-to-end deep multimodal convolutional-recurrent network for learning both vision and language representations simultaneously to infer image-text similarity. The model learns which pairs are a match (positive) and which ones are a mismatch (negative) using a hinge-based triplet ranking. To learn about the joint representations, we leverage our newly extracted collection of tweets from Twitter. The main characteristic of our dataset is that the images and tweets are not standardized the same as the benchmarks. Furthermore, there can be a higher semantic correlation between the pictures and tweets contrary to benchmarks in which the descriptions are well-organized. Experimental results on MS-COCO benchmark dataset show that our model outperforms certain methods presented previously and has competitive performance compared to the state-of-the-art. The code and dataset have been made available publicly.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge