Deep Attributes from Context-Aware Regional Neural Codes
Paper and Code
Sep 08, 2015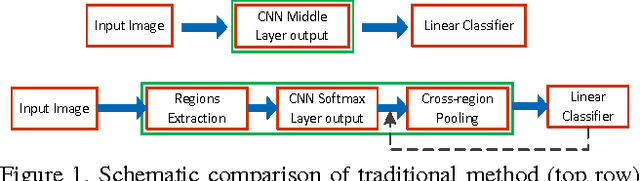
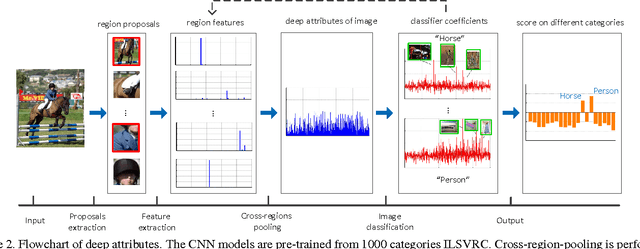
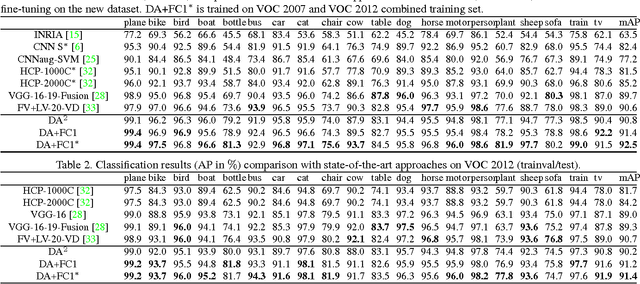
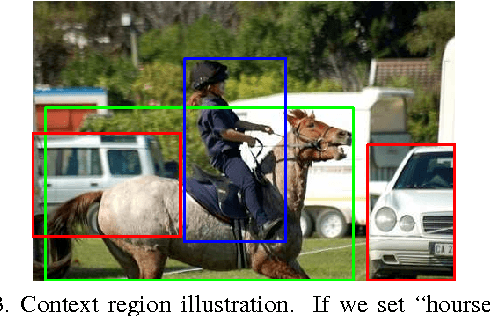
Recently, many researches employ middle-layer output of convolutional neural network models (CNN) as features for different visual recognition tasks. Although promising results have been achieved in some empirical studies, such type of representations still suffer from the well-known issue of semantic gap. This paper proposes so-called deep attribute framework to alleviate this issue from three aspects. First, we introduce object region proposals as intermedia to represent target images, and extract features from region proposals. Second, we study aggregating features from different CNN layers for all region proposals. The aggregation yields a holistic yet compact representation of input images. Results show that cross-region max-pooling of soft-max layer output outperform all other layers. As soft-max layer directly corresponds to semantic concepts, this representation is named "deep attributes". Third, we observe that only a small portion of generated regions by object proposals algorithm are correlated to classification target. Therefore, we introduce context-aware region refining algorithm to pick out contextual regions and build context-aware classifiers. We apply the proposed deep attributes framework for various vision tasks. Extensive experiments are conducted on standard benchmarks for three visual recognition tasks, i.e., image classification, fine-grained recognition and visual instance retrieval. Results show that deep attribute approaches achieve state-of-the-art results, and outperforms existing peer methods with a significant margin, even though some benchmarks have little overlap of concepts with the pre-trained CNN models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge