Decompose, Enrich, and Extract! Schema-aware Event Extraction using LLMs
Paper and Code
Jun 03, 2024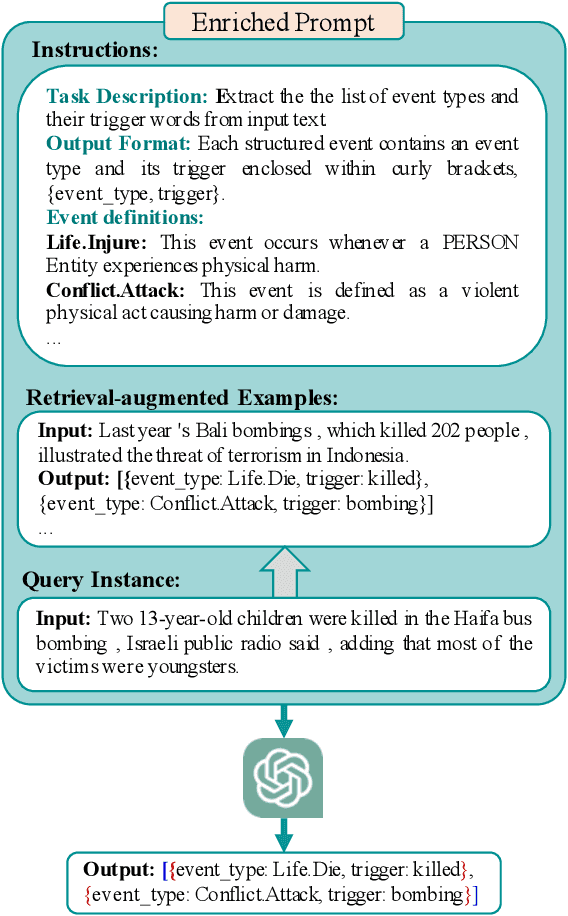
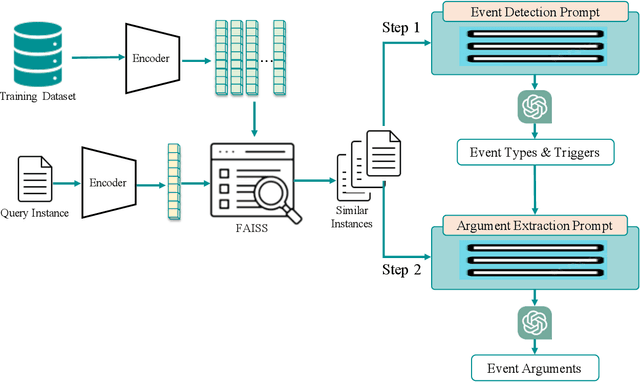


Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate significant capabilities in processing natural language data, promising efficient knowledge extraction from diverse textual sources to enhance situational awareness and support decision-making. However, concerns arise due to their susceptibility to hallucination, resulting in contextually inaccurate content. This work focuses on harnessing LLMs for automated Event Extraction, introducing a new method to address hallucination by decomposing the task into Event Detection and Event Argument Extraction. Moreover, the proposed method integrates dynamic schema-aware augmented retrieval examples into prompts tailored for each specific inquiry, thereby extending and adapting advanced prompting techniques such as Retrieval-Augmented Generation. Evaluation findings on prominent event extraction benchmarks and results from a synthesized benchmark illustrate the method's superior performance compared to baseline approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge