Data Generation via Latent Factor Simulation for Fairness-aware Re-ranking
Paper and Code
Sep 21, 2024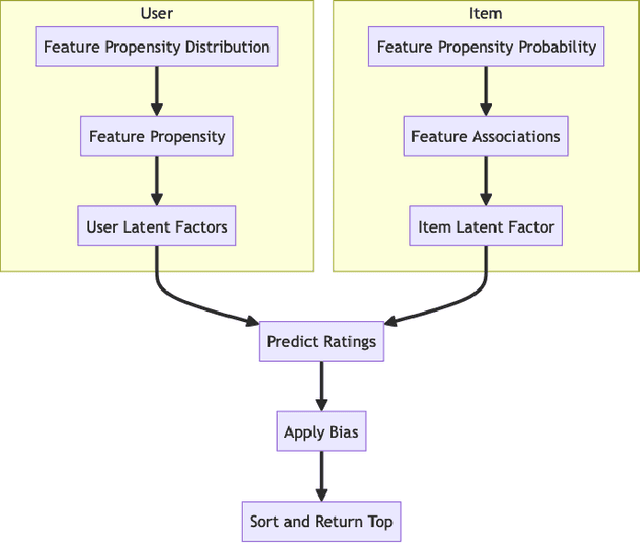

Synthetic data is a useful resource for algorithmic research. It allows for the evaluation of systems under a range of conditions that might be difficult to achieve in real world settings. In recommender systems, the use of synthetic data is somewhat limited; some work has concentrated on building user-item interaction data at large scale. We believe that fairness-aware recommendation research can benefit from simulated data as it allows the study of protected groups and their interactions without depending on sensitive data that needs privacy protection. In this paper, we propose a novel type of data for fairness-aware recommendation: synthetic recommender system outputs that can be used to study re-ranking algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge