Data-Centric Machine Learning in the Legal Domain
Paper and Code
Jan 17, 2022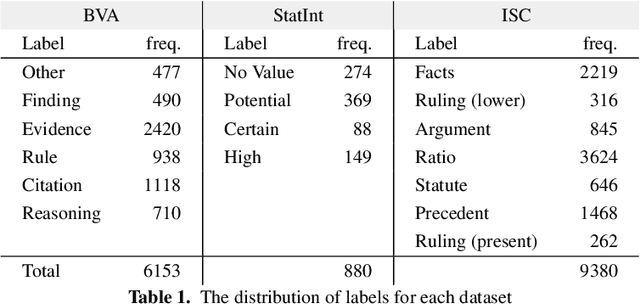
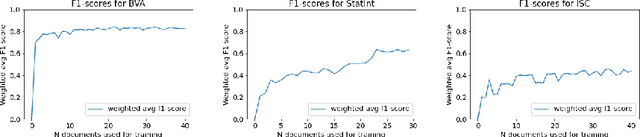
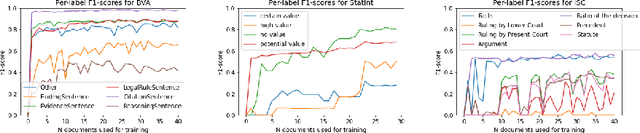
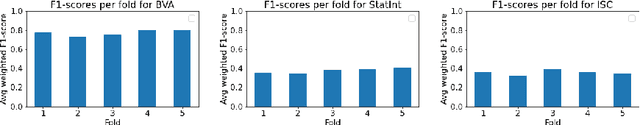
Machine learning research typically starts with a fixed data set created early in the process. The focus of the experiments is finding a model and training procedure that result in the best possible performance in terms of some selected evaluation metric. This paper explores how changes in a data set influence the measured performance of a model. Using three publicly available data sets from the legal domain, we investigate how changes to their size, the train/test splits, and the human labelling accuracy impact the performance of a trained deep learning classifier. We assess the overall performance (weighted average) as well as the per-class performance. The observed effects are surprisingly pronounced, especially when the per-class performance is considered. We investigate how "semantic homogeneity" of a class, i.e., the proximity of sentences in a semantic embedding space, influences the difficulty of its classification. The presented results have far reaching implications for efforts related to data collection and curation in the field of AI & Law. The results also indicate that enhancements to a data set could be considered, alongside the advancement of the ML models, as an additional path for increasing classification performance on various tasks in AI & Law. Finally, we discuss the need for an established methodology to assess the potential effects of data set properties.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge