Cross-Modal Synthesis of Structural MRI and Functional Connectivity Networks via Conditional ViT-GANs
Paper and Code
Sep 15, 2023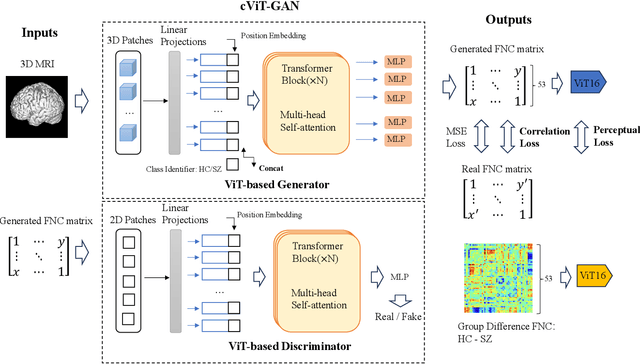
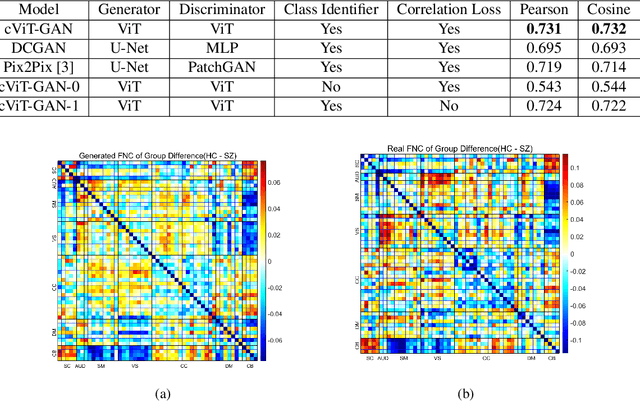
The cross-modal synthesis between structural magnetic resonance imaging (sMRI) and functional network connectivity (FNC) is a relatively unexplored area in medical imaging, especially with respect to schizophrenia. This study employs conditional Vision Transformer Generative Adversarial Networks (cViT-GANs) to generate FNC data based on sMRI inputs. After training on a comprehensive dataset that included both individuals with schizophrenia and healthy control subjects, our cViT-GAN model effectively synthesized the FNC matrix for each subject, and then formed a group difference FNC matrix, obtaining a Pearson correlation of 0.73 with the actual FNC matrix. In addition, our FNC visualization results demonstrate significant correlations in particular subcortical brain regions, highlighting the model's capability of capturing detailed structural-functional associations. This performance distinguishes our model from conditional CNN-based GAN alternatives such as Pix2Pix. Our research is one of the first attempts to link sMRI and FNC synthesis, setting it apart from other cross-modal studies that concentrate on T1- and T2-weighted MR images or the fusion of MRI and CT scans.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge