Cross-Modal Multi-Tasking for Speech-to-Text Translation via Hard Parameter Sharing
Paper and Code
Sep 27, 2023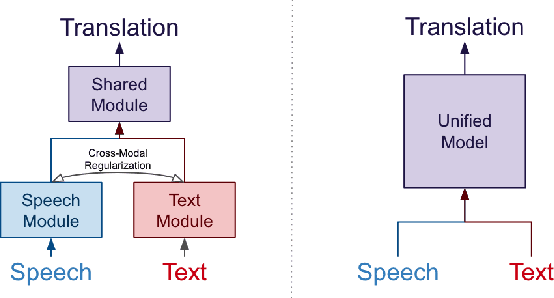

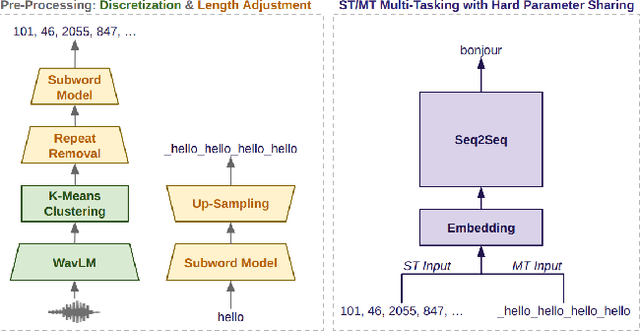

Recent works in end-to-end speech-to-text translation (ST) have proposed multi-tasking methods with soft parameter sharing which leverage machine translation (MT) data via secondary encoders that map text inputs to an eventual cross-modal representation. In this work, we instead propose a ST/MT multi-tasking framework with hard parameter sharing in which all model parameters are shared cross-modally. Our method reduces the speech-text modality gap via a pre-processing stage which converts speech and text inputs into two discrete token sequences of similar length -- this allows models to indiscriminately process both modalities simply using a joint vocabulary. With experiments on MuST-C, we demonstrate that our multi-tasking framework improves attentional encoder-decoder, Connectionist Temporal Classification (CTC), transducer, and joint CTC/attention models by an average of +0.5 BLEU without any external MT data. Further, we show that this framework incorporates external MT data, yielding +0.8 BLEU, and also improves transfer learning from pre-trained textual models, yielding +1.8 BLEU.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge