Cross-Descriptor Visual Localization and Mapping
Paper and Code
Dec 02, 2020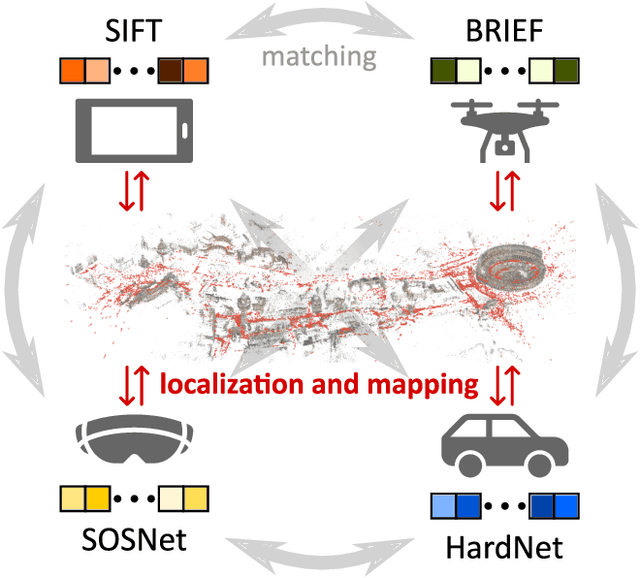
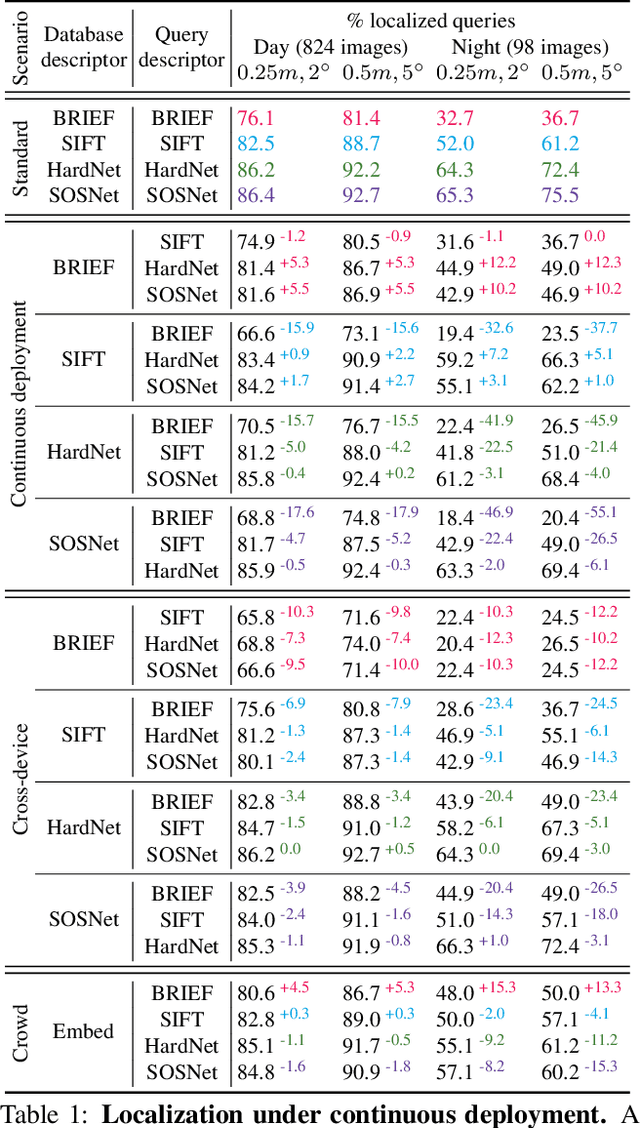
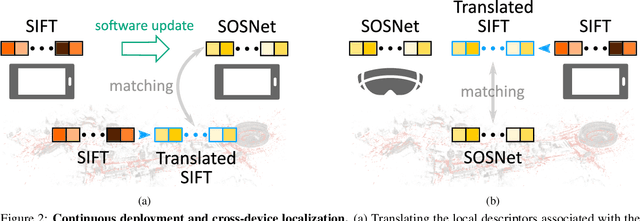
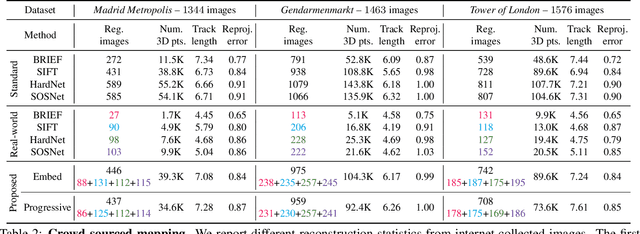
Visual localization and mapping is the key technology underlying the majority of Mixed Reality and robotics systems. Most state-of-the-art approaches rely on local features to establish correspondences between images. In this paper, we present three novel scenarios for localization and mapping which require the continuous update of feature representations and the ability to match across different feature types. While localization and mapping is a fundamental computer vision problem, the traditional setup treats it as a single-shot process using the same local image features throughout the evolution of a map. This assumes the whole process is repeated from scratch whenever the underlying features are changed. However, reiterating it is typically impossible in practice, because raw images are often not stored and re-building the maps could lead to loss of the attached digital content. To overcome the limitations of current approaches, we present the first principled solution to cross-descriptor localization and mapping. Our data-driven approach is agnostic to the feature descriptor type, has low computational requirements, and scales linearly with the number of description algorithms. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach on state-of-the-art benchmarks for a variety of handcrafted and learned features.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge