Creating synthetic energy meter data using conditional diffusion and building metadata
Paper and Code
Mar 31, 2024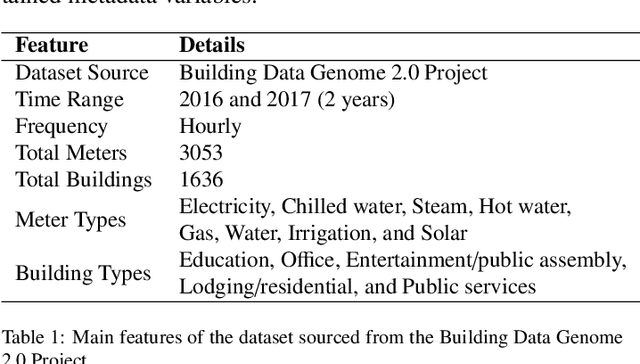
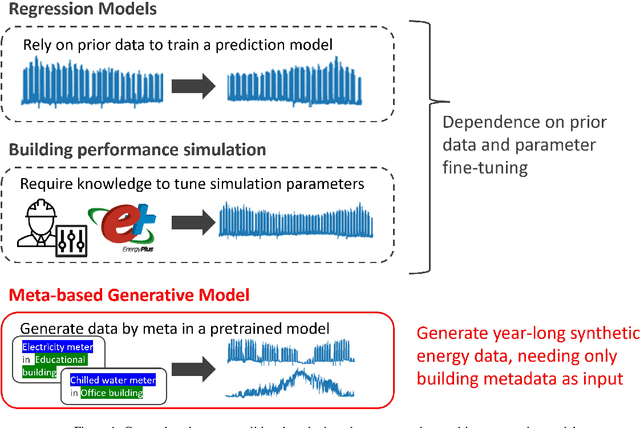
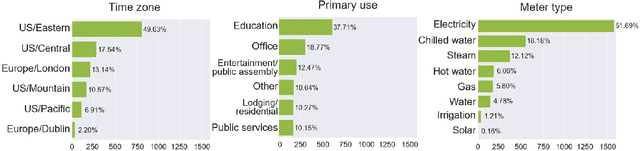
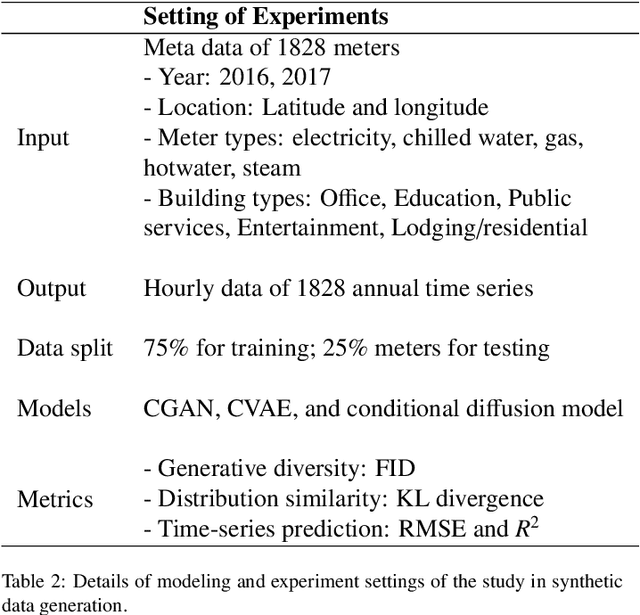
Advances in machine learning and increased computational power have driven progress in energy-related research. However, limited access to private energy data from buildings hinders traditional regression models relying on historical data. While generative models offer a solution, previous studies have primarily focused on short-term generation periods (e.g., daily profiles) and a limited number of meters. Thus, the study proposes a conditional diffusion model for generating high-quality synthetic energy data using relevant metadata. Using a dataset comprising 1,828 power meters from various buildings and countries, this model is compared with traditional methods like Conditional Generative Adversarial Networks (CGAN) and Conditional Variational Auto-Encoders (CVAE). It explicitly handles long-term annual consumption profiles, harnessing metadata such as location, weather, building, and meter type to produce coherent synthetic data that closely resembles real-world energy consumption patterns. The results demonstrate the proposed diffusion model's superior performance, with a 36% reduction in Frechet Inception Distance (FID) score and a 13% decrease in Kullback-Leibler divergence (KL divergence) compared to the following best method. The proposed method successfully generates high-quality energy data through metadata, and its code will be open-sourced, establishing a foundation for a broader array of energy data generation models in the future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge