Cramer-Rao Bounds for Near-Field Sensing: A Generic Modular Architecture
Paper and Code
Apr 11, 2024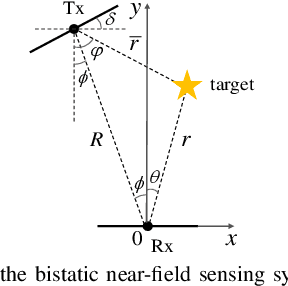
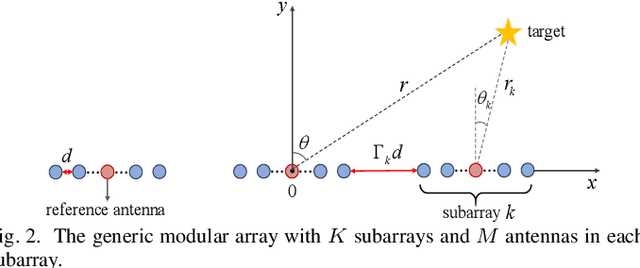
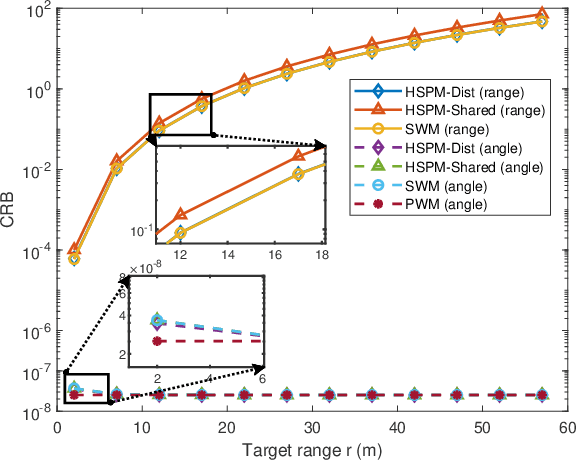
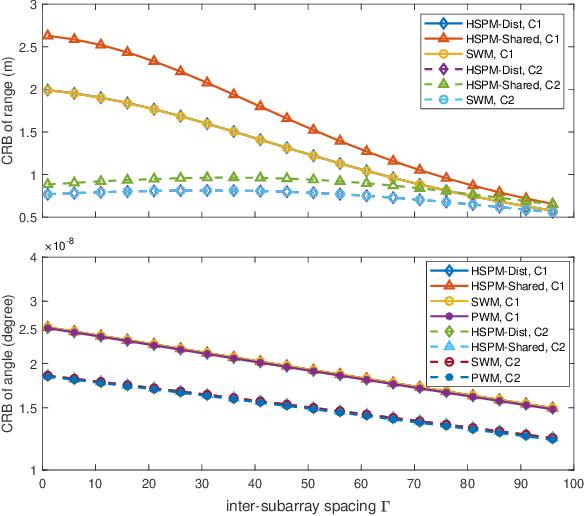
A generic modular array architecture is proposed, featuring uniform/non-uniform subarray layouts that allows for flexible deployment. The bistatic near-field sensing system is considered, where the target is located in the near-field of the whole modular array and the far-field of each subarray. Then, the closed-form expressions of Cramer-Rao bounds (CRBs) for range and angle estimations are derived based on the hybrid spherical and planar wave model (HSPM). Simulation results validate the accuracy of the derived closed-form CRBs and demonstrate that: i) The HSPM with varying angles of arrival (AoAs) between subarrays can reduce the CRB for range estimation compared to the traditional HSPM with shared AoA; and ii) The proposed generic modular architecture with subarrays positioned closer to the edges can significantly reduce the CRBs compared to the traditional modular architecture with uniform subarray layout, when the array aperture is fixed.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge