Covariance-Robust Dynamic Watermarking
Paper and Code
Mar 31, 2020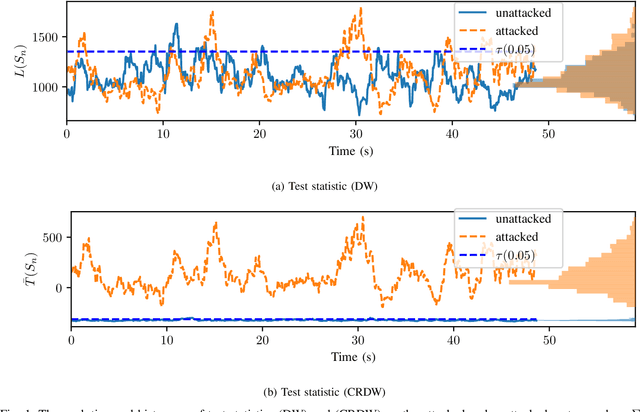
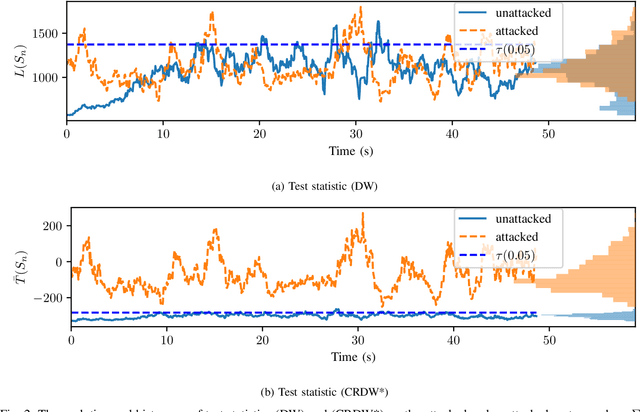
Attack detection and mitigation strategies for cyberphysical systems (CPS) are an active area of research, and researchers have developed a variety of attack-detection tools such as dynamic watermarking. However, such methods often make assumptions that are difficult to guarantee, such as exact knowledge of the distribution of measurement noise. Here, we develop a new dynamic watermarking method that we call covariance-robust dynamic watermarking, which is able to handle uncertainties in the covariance of measurement noise. Specifically, we consider two cases. In the first this covariance is fixed but unknown, and in the second this covariance is slowly-varying. For our tests, we only require knowledge of a set within which the covariance lies. Furthermore, we connect this problem to that of algorithmic fairness and the nascent field of fair hypothesis testing, and we show that our tests satisfy some notions of fairness. Finally, we exhibit the efficacy of our tests on empirical examples chosen to reflect values observed in a standard simulation model of autonomous vehicles.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge