Correcting inter-scan motion artefacts in quantitative R1 mapping at 7T
Paper and Code
Aug 24, 2021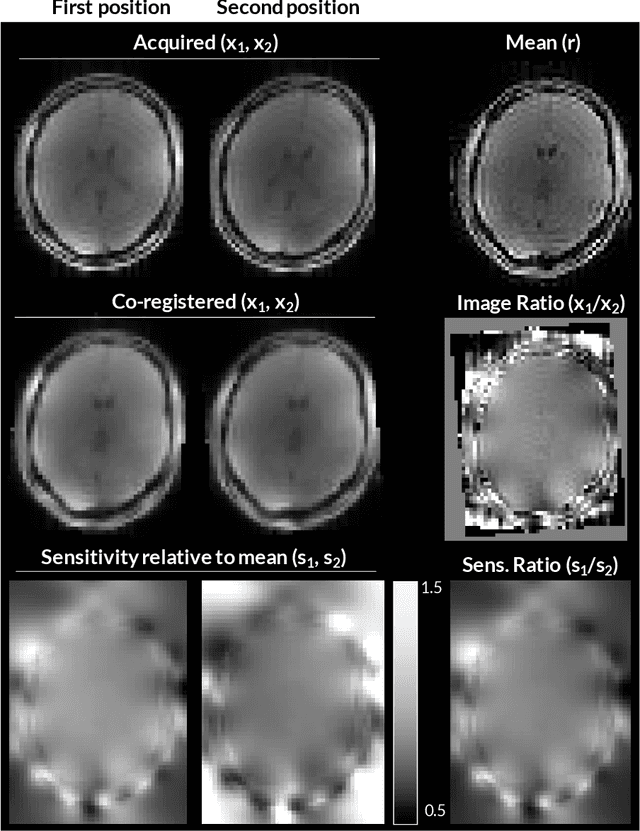
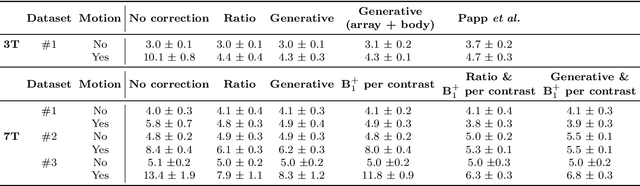
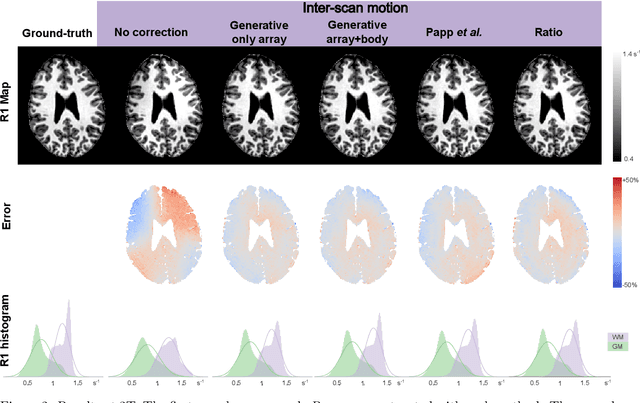
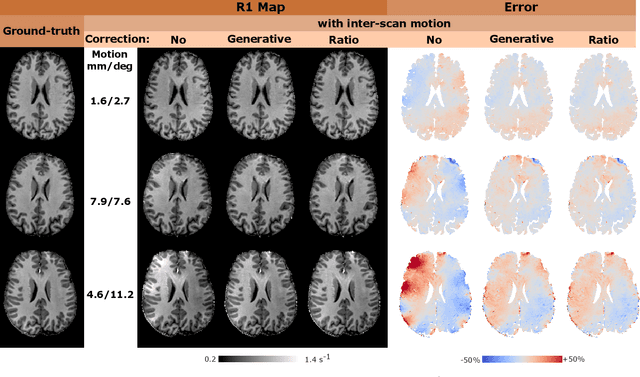
Purpose: Inter-scan motion is a substantial source of error in $R_1$ estimation, and can be expected to increase at 7T where $B_1$ fields are more inhomogeneous. The established correction scheme does not translate to 7T since it requires a body coil reference. Here we introduce two alternatives that outperform the established method. Since they compute relative sensitivities they do not require body coil images. Theory: The proposed methods use coil-combined magnitude images to obtain the relative coil sensitivities. The first method efficiently computes the relative sensitivities via a simple ratio; the second by fitting a more sophisticated generative model. Methods: $R_1$ maps were computed using the variable flip angle (VFA) approach. Multiple datasets were acquired at 3T and 7T, with and without motion between the acquisition of the VFA volumes. $R_1$ maps were constructed without correction, with the proposed corrections, and (at 3T) with the previously established correction scheme. Results: At 3T, the proposed methods outperform the baseline method. Inter-scan motion artefacts were also reduced at 7T. However, reproducibility only converged on that of the no motion condition if position-specific transmit field effects were also incorporated. Conclusion: The proposed methods simplify inter-scan motion correction of $R_1$ maps and are applicable at both 3T and 7T, where a body coil is typically not available. The open-source code for all methods is made publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge