Convergence Rates for the MAP of an Exponential Family and Stochastic Mirror Descent -- an Open Problem
Paper and Code
Nov 12, 2021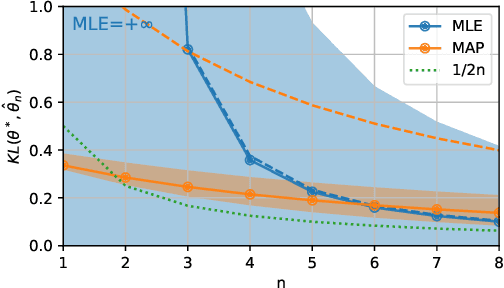
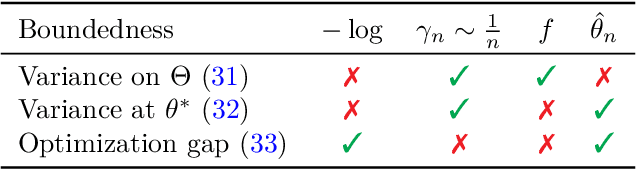
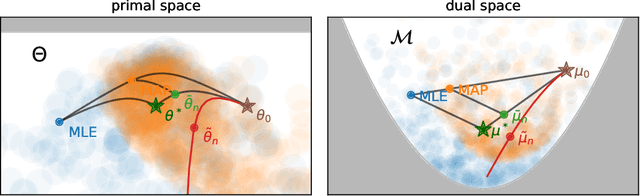
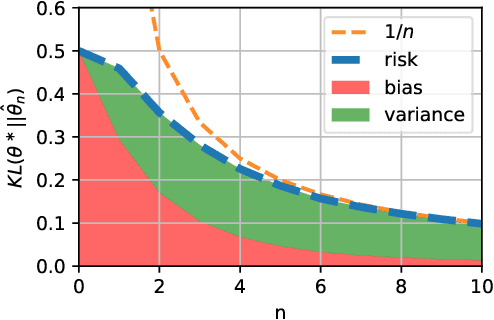
We consider the problem of upper bounding the expected log-likelihood sub-optimality of the maximum likelihood estimate (MLE), or a conjugate maximum a posteriori (MAP) for an exponential family, in a non-asymptotic way. Surprisingly, we found no general solution to this problem in the literature. In particular, current theories do not hold for a Gaussian or in the interesting few samples regime. After exhibiting various facets of the problem, we show we can interpret the MAP as running stochastic mirror descent (SMD) on the log-likelihood. However, modern convergence results do not apply for standard examples of the exponential family, highlighting holes in the convergence literature. We believe solving this very fundamental problem may bring progress to both the statistics and optimization communities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge