Contrastive Factor Analysis
Paper and Code
Aug 01, 2024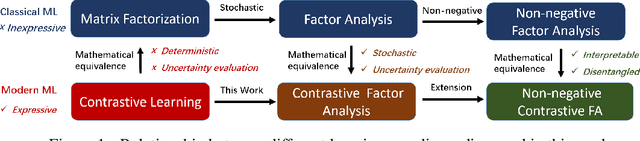



Factor analysis, often regarded as a Bayesian variant of matrix factorization, offers superior capabilities in capturing uncertainty, modeling complex dependencies, and ensuring robustness. As the deep learning era arrives, factor analysis is receiving less and less attention due to their limited expressive ability. On the contrary, contrastive learning has emerged as a potent technique with demonstrated efficacy in unsupervised representational learning. While the two methods are different paradigms, recent theoretical analysis has revealed the mathematical equivalence between contrastive learning and matrix factorization, providing a potential possibility for factor analysis combined with contrastive learning. Motivated by the interconnectedness of contrastive learning, matrix factorization, and factor analysis, this paper introduces a novel Contrastive Factor Analysis framework, aiming to leverage factor analysis's advantageous properties within the realm of contrastive learning. To further leverage the interpretability properties of non-negative factor analysis, which can learn disentangled representations, contrastive factor analysis is extended to a non-negative version. Finally, extensive experimental validation showcases the efficacy of the proposed contrastive (non-negative) factor analysis methodology across multiple key properties, including expressiveness, robustness, interpretability, and accurate uncertainty estimation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge