Conditional entropy minimization principle for learning domain invariant representation features
Paper and Code
Jan 25, 2022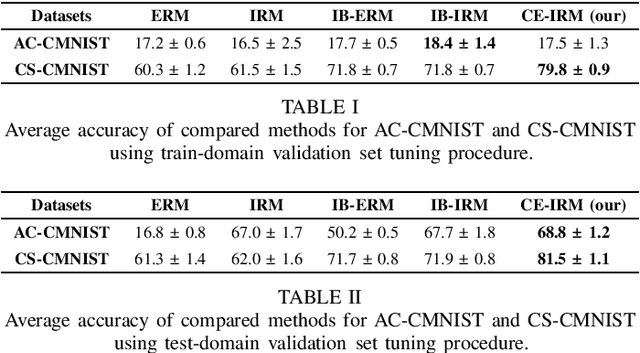
Invariance principle-based methods, for example, Invariant Risk Minimization (IRM), have recently emerged as promising approaches for Domain Generalization (DG). Despite the promising theory, invariance principle-based approaches fail in common classification tasks due to the mixture of the true invariant features and the spurious invariant features. In this paper, we propose a framework based on the conditional entropy minimization principle to filter out the spurious invariant features leading to a new algorithm with a better generalization capability. We theoretically prove that under some particular assumptions, the representation function can precisely recover the true invariant features. In addition, we also show that the proposed approach is closely related to the well-known Information Bottleneck framework. Both the theoretical and numerical results are provided to justify our approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge