Comparing Alternative Route Planning Techniques: A Web-based Demonstration and User Study
Paper and Code
Jun 15, 2020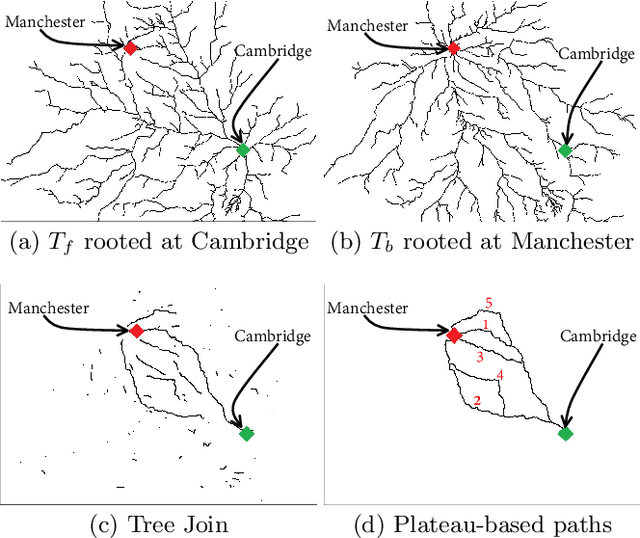
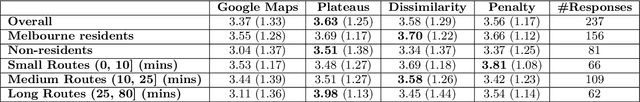
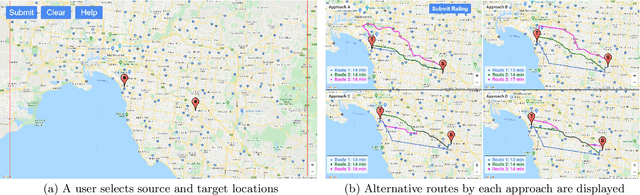
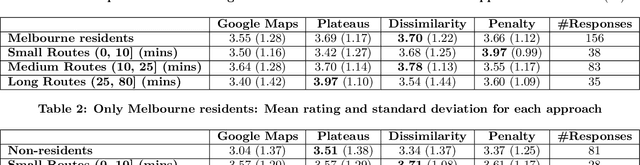
Due to the popularity of smartphones, cheap wireless networks and availability of road network data, navigation applications have become a part of our everyday life. Many modern navigation systems and map-based services do not only provide the fastest route from a source location s to a target location t but also provide a few alternative routes to the users as more options to choose from. Consequently, computing alternative paths from a source s to a target t has received significant research attention in the past few years. However, it is not clear which of the existing approaches generates alternative paths of better quality because the quality of these alternatives is mostly subjective. Motivated by this, in this paper, we present the first user study that compares the quality of the alternative routes generated by four of the most popular existing approaches including the routes provided by Google Maps. We also present the details of a web-based demo system that can be accessed using any internet enabled device and allows users to see the alternative routes generated by the four approaches for any pair of source and target selected by the users. Our user study shows that although the mean rating received by Google Maps is slightly lower than the mean ratings received by the other three approaches, the results are not statistically significant. We also discuss the limitations of this user study and recommend the readers to interpret these results with caution because certain factors beyond our control may have affected the participants' ratings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge