ColDE: A Depth Estimation Framework for Colonoscopy Reconstruction
Paper and Code
Nov 19, 2021
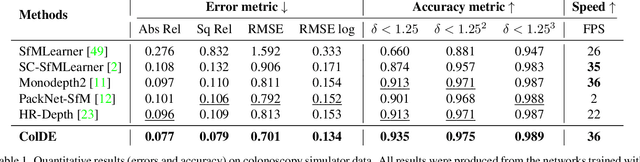
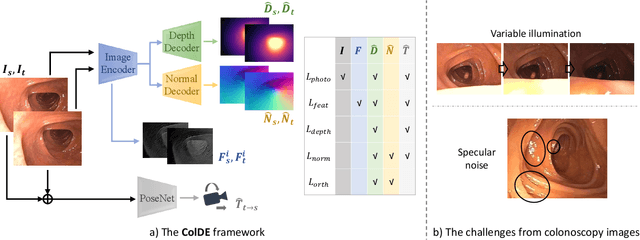
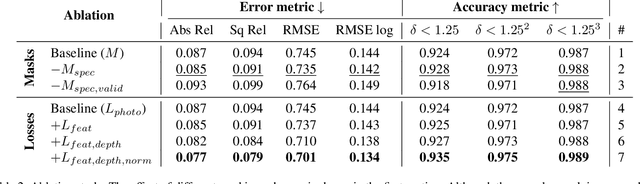
One of the key elements of reconstructing a 3D mesh from a monocular video is generating every frame's depth map. However, in the application of colonoscopy video reconstruction, producing good-quality depth estimation is challenging. Neural networks can be easily fooled by photometric distractions or fail to capture the complex shape of the colon surface, predicting defective shapes that result in broken meshes. Aiming to fundamentally improve the depth estimation quality for colonoscopy 3D reconstruction, in this work we have designed a set of training losses to deal with the special challenges of colonoscopy data. For better training, a set of geometric consistency objectives was developed, using both depth and surface normal information. Also, the classic photometric loss was extended with feature matching to compensate for illumination noise. With the training losses powerful enough, our self-supervised framework named ColDE is able to produce better depth maps of colonoscopy data as compared to the previous work utilizing prior depth knowledge. Used in reconstruction, our network is able to reconstruct good-quality colon meshes in real-time without any post-processing, making it the first to be clinically applicable.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge